OCI Image Specification V1.1.1
Image Format Specification(镜像格式规范)
This specification defines an OCI Image, consisting of an image manifest, an image index (optional), a set of filesystem layers, and a configuration.
规范定义了一个符合OCI规范的镜像,都是由一个镜像manifest文件,一个镜像索引,镜像层文件系统变更集和配置构成。
The goal of this specification is to enable the creation of interoperable tools for building, transporting, and preparing a container image to run.
规范的目标是创建一个可交互的工具,该工具可用于构建,传输和准备要运行的容器镜像。
1 Notational Conventions(符号约定)
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “NOT RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119 (Bradner, S., “Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels”, BCP 14, RFC 2119, March 1997).
关键词 “MUST” (必须), “MUST NOT” (禁止), “REQUIRED” (必要的), “SHALL” , “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”(应该), “SHOULD NOT”(不应该), “RECOMMENDED” (建议), “NOT RECOMMENDED” (不建议), “MAY” (可能), “OPTIONAL” (可选的) 将按照 RFC 2119 中的描述进行解释。(参见:RFC2119:表示要求的动词)
The key words “unspecified”, “undefined”, and “implementation-defined” are to be interpreted as described in the rationale for the C99 standard.
关键词 “未指明”、“未定义” 和 “实现定义” 应按照 C99 标准的基本原理中所描述的方式进行解释。
An implementation is not compliant if it fails to satisfy one or more of the MUST, MUST NOT, REQUIRED, SHALL, or SHALL NOT requirements for the protocols it implements. An implementation is compliant if it satisfies all the MUST, MUST NOT, REQUIRED, SHALL, and SHALL NOT requirements for the protocols it implements.
若某个实现方案未能满足其所实现协议中一项或多项 MUST、MUST NOT、REQUIRED、SHALL 或 SHALL NOT 要求,则该实现方案不具备合规性。若某个实现方案满足了其实现协议中所有 MUST、MUST NOT、REQUIRED、SHALL 和 SHALL NOT 要求,则该实现方案具备合规性。
2 Overview(概览)
原文:
At a high level the image manifest contains metadata about the contents and dependencies of the image including the content-addressable identity of one or more filesystem layer changeset archives that will be unpacked to make up the final runnable filesystem. The image configuration includes information such as application arguments, environments, etc. The image index is a higher-level manifest which points to a list of manifests and descriptors. Typically, these manifests may provide different implementations of the image, possibly varying by platform or other attributes.
从更高的维度来看,一个镜像的Manifest文件包含了镜像内容和依赖的元数据的信息。这些元数据内容通常包括了一个或者是多个指向filesystem layer变更集的归档文件(这些文件解压缩后可以用于构成最终可用于运行的文件系统)的内容可寻址标识符。Image 配置 包括应用参数、环境变量等信息。镜像索引是一个更高级别的 manifest,它指向一连串manifests和它们的描述符的列表。通常情况下,镜像索 可以提供的是操作系统或者硬件架构不同导致的镜像的不同实现(译者注:不同的平台存在不同的镜像)
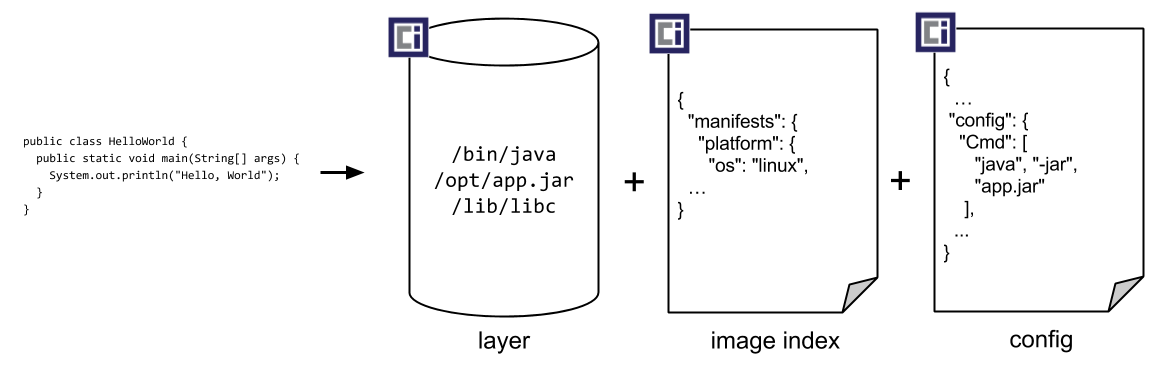
Once built the OCI Image can then be discovered by name, downloaded, verified by hash, trusted through a signature, and unpacked into an OCI Runtime Bundle.
构建OCI镜像完成后,就可以通过名称来发现、下载、通过哈希验证、通过签名信任,,并解压到 OCI 运行时包中。
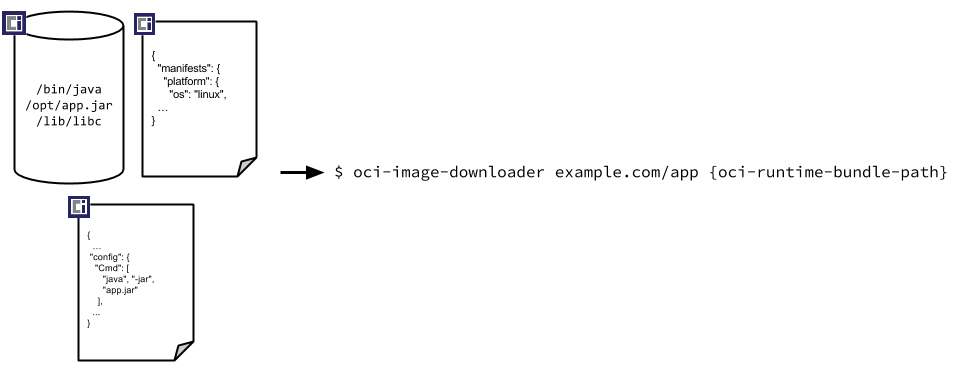
2.1 Understanding the Specification(理解规范)
The OCI Image Media Types document is a starting point to understanding the overall structure of the specification.
OCI 镜像的媒体类型文档是规范整体结构的起点。
The high-level components of the spec include:
该规范的顶层组件包括:
Image Manifest - a document describing the components that make up a container image
镜像 Manifest - 描述构成容器镜像的组件
Image Index - an annotated list of manifests
镜像索引 - 一个注解的 镜像 Manifest 的索引
Image Layout - a filesystem layout representing the contents of an image
Image Layout - 描述一个镜像在文件系统中的布局情况
Filesystem Layer - a changeset that describes a container’s filesystem
Filesystem Layer - 描述容器文件系统的变更集
Image Configuration - a document determining layer ordering and configuration of the image suitable for translation into a runtime bundle
Image 配置 - 转换为运行时 bundle 的镜像的层排序和配置
Conversion - a document describing how this translation should occur
Conversion - 转换应该如何发生
Artifacts Guidance - a document describing how to use the spec for packaging content other than OCI images
制品指南(Artifacts Guidance)—— 一份描述如何使用本规范打包非 OCI 镜像内容的文档
Descriptor - a reference that describes the type, metadata and content address of referenced content
描述符(Descriptor)—— 一种引用,用于描述被引用内容的类型、元数据和内容地址
Future versions of this specification may include the following OPTIONAL features:
本规范的未来版本可能包括以下可选功能:
Signatures that are based on signing image content address
基于签名镜像内容地址的签名
Naming that is federated based on DNS and can be delegated
基于 DNS 联合且可委托的命名
2.2 OCI Image Media Types (OCI镜像媒体类型)
The following media types identify the formats described here and their referenced resources:
以下 媒体类型 标识此处描述的格式及其参考文档的链接:
application/vnd.oci.descriptor.v1+json: Content Descriptor(https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/descriptor.md)application/vnd.oci.layout.header.v1+json: OCI Layout(https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/image-layout.md)application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json: Image Index( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/image-index.md)application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json: Image manifest( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/manifest.md)application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json: Image config( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/config.md)application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar: “Layer”, as a tar archive( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/layer.md)application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip: “Layer”, as a tar archive compressed with gzip( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/layer.md)application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+zstd: “Layer”, as a tar archive compressed with zstd)( https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/layer.md)application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json: Empty for unused descriptors (https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/v1.1.1/layer.md)
The following media types identify a “Layer” with distribution restrictions, but are deprecated and not recommended for future use:
以下媒体类型标识具有分发限制的 “层(Layer)”,但这些类型已被弃用,不建议在未来使用:
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar: “Layer”, as a tar archiveapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip: “Layer”, as a tar archive with distribution restrictions compressed with gzipapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd: “Layer”, as a tar archive with distribution restrictions compressed with zstd
2.2.1 Media Type Conflicts(媒体类型冲突)
Blob retrieval methods MAY return media type metadata. For example, a HTTP response might return a manifest with the Content-Type header set to application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json. Implementations MAY also have expectations for the blob’s media type and digest (e.g. from a descriptor referencing the blob).
Blob的检索方式可能会返回元数据的类型。举个例子,一个HTTP返回的可能是一个请求头Content-Type被设置成application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json的返回。实现对Blob的媒体类型和摘要期望(例如来自引用 blob 的描述符)。
Implementations that do not have an expected media type for the blob SHOULD respect the returned media type.
*实现(译者注: 这里特指容器运行时或者镜像仓库具体的服务,本小节内的实现语义均与当前语义等同)对Blob没有预设的媒体类型和期望时,应当遵从索引该Blob时返回的媒体类型的元数据。*
Implementations that have an expected media type which matches the returned media type SHOULD respect the matched media type.
*实现对Blob存在预设的媒体类型和期望时,并且该期望与检索Blob返回的媒体类型元数据一致时,应该遵从这一匹配的媒体类型。*
Implementations that have an expected media type which does not match the returned media type SHOULD:
实现对Blob存在的预设的媒体类型和期望,并且该期望与检索Blob返回的媒体类型元数据不一致时,有如下的三种情况:
Respect the expected media type if the blob matches the expected digest. Implementations MAY warn about the media type mismatch.
如果Blob的内容匹配预期的摘要内容,则遵从预期的媒体类型内容。实现可能需要有关于媒体类型不匹配的警告提示。
Return an error if the blob does not match the expected digest (as recommended for descriptors).
如果Blob的内容与预期的摘要内容并不匹配,则应该返回一个媒体类型不匹配的错误内容。
Return an error if they do not have an expected digest.
如果没有获取到对当前Blob的预期摘要,则应该返回一个错误。
2.2.2 Compatibility Matrix(兼容性矩阵)
The OCI Image Specification strives to be backwards and forwards compatible when possible. Breaking compatibility with existing systems creates a burden on users whether they are build systems, distribution systems, container engines, etc. This section shows where the OCI Image Specification is compatible with formats external to the OCI Image and different versions of this specification.
OCI Image Specification尽最大的可能保证前后的兼容性。破坏与现有系统的兼容性会给用户带来负担,无论是用户处于构建系统,分发系统亦或者是容器引擎等。本小结将说明OCI镜像规范与OCI镜像的外部格式以及不同版本之间的兼容性。
application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json
Similar/related schema:
类似的/关联的提要:
- application/vnd.docker.distribution.manifest.list.v2+json
.annotations: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中.[]manifests.annotations: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中.[]manifests.urls: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中
application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json
Similar/related schema:
类似的/关联的提要:
- application/vnd.docker.distribution.manifest.v2+json
.annotations: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中.config.annotations: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中.config.urls: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中.[]layers.annotations: only present in OCI 当前只存在于OCI中
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip
Interchangeable and fully compatible mime-types:
可互换且完全兼容的 MIME 类型:
application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json
Similar/related schema:
类似的/关联的提要:
application/vnd.docker.container.image.v1+json
(Docker Image Spec v1.2)
.config.Memory: only present in Docker, and reserved in OCI 只应用于Docker Image Spec中,但是OCI中还是给与保留.config.MemorySwap: only present in Docker, and reserved in OCI 只应用于Docker Image Spec中,但是OCI中还是给与保留.config.CpuShares: only present in Docker, and reserved in OCI 只应用于Docker Image Spec中,但是OCI中还是给与保留.config.Healthcheck: only present in Docker, and reserved in OCI 只应用于Docker Image Spec中,但是OCI中还是给与保留
Moby/Docker
.config.ArgsEscaped: Windows-specific Moby/Docker extension, deprecated in OCI, available for compatibility with older images..config.ArgsEscaped: 特定于 Windows 系统的 Moby/Docker 扩展,在 OCI 中已弃用,仅为兼容旧镜像而保留。
.config.StopSignal and .config.Labels are accidentally undocumented in Docker Image Spec v1.2, but these fields are not OCI-specific concepts.
.config.StopSignal 和 .config.Labels 在 Docker 镜像规范 v1.2 中意外未被记录,但这些字段并非 OCI 特有的概念。
译者注:
本小结提到的兼容性声明,大家可以去阅读一下Docker的Moby的源码,从代码中可以更加直观的理解这一部分。这部分兼容声明存在客观历史原因,因为在上一篇<<OCI Image Format Specification Part1-物理解剖容器Image>>中笔者有提到过Docker于OCI的关系,因为Docker从时间线上早于OCI标准制定的时间,但是同时Docker又成为了当时的事实标准,所以,在OCI于Docker的博弈中,OCI Image Spec给出了兼容性声明,明确可以兼容Docker的Image Spec,同时Docker公司也认可了OCI的规范。
2.3 Relations(层级关系)
The following figure shows how the above media types reference each other:
下面的图片展示了上层的不同媒体类型之间的引用关系:
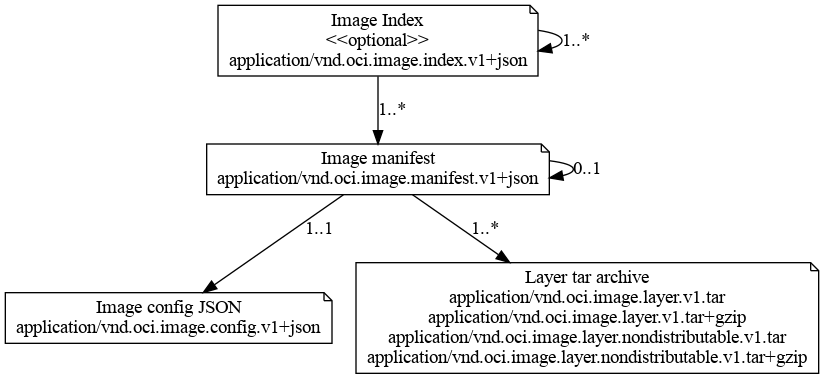
Descriptors are used for all references. The image-index being a “fat manifest” references a list of image manifests per target platform. An image manifest references exactly one target configuration and possibly many layers.
所有的描述符均通过引用实现。image-index作为一份”胖清单”的镜像索引,会按照目标平台引用一系列的镜像清单列表。这一系列的清单列表中的任意一份清单都会精确的引用指定清单的目标配置,并且指出所有可能的容器镜像层。
译者注:
这部分的内容大家可以参考上一篇<<OCI Image Format Specification Part1-物理解剖容器Image>>的内容来加深理解,busybox的镜像如何通过index.json找到了镜像的manifest,同时又通过镜像的manifest找到了镜像配置以及镜像的文件系统层。
3. OCI Content Descriptors (OCI内容描述符)
An OCI image consists of several different components, arranged in a Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
一个OCI镜像由多个不同的组件构成,这些内容共同构成了一个默克尔有向无环图(wiki链接:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree)。
References between components in the graph are expressed through Content Descriptors.
组件之间的引用关系在图中都通过内容描述符来实现。
A Content Descriptor (or simply Descriptor) describes the disposition of the targeted content.
内容描述符用于描述目标的内容和状态。
A Content Descriptor includes the type of the content, a content identifier (digest), and the byte-size of the raw content. Optionally, it includes the type of artifact it is describing.
内容描述符包含了内容的类型,内容的摘要,以及原始内容的大小。此外,它还可选择性的包含所描述的制品的类型。
Descriptors SHOULD be embedded in other formats to securely reference external content.
描述符应该内嵌到其他格式中,以安全的引用外部内容。
Other formats SHOULD use descriptors to securely reference external content.
其他的格式应该使用描述符去安全的引用外部的内容。
When other formats contain multiple descriptors, unless otherwise specified, those descriptors are independent of each other, allowing fields like the
mediaTypeand the algorithm for thedigestto vary within that external content.当其他的格式包含多个描述符的时候,除非特殊指定,否则这些描述符是相互独立的,允许字段如媒体类型和算法摘要在外部内容表示的时候是不同的。
This section defines the application/vnd.oci.descriptor.v1+json media type.
本小节用于定义application/vnd.oci.descriptor.v1+json媒体类型
译者注:
因为镜像的组成声明了使用默克尔有向无环图,所以每个组件(如清单、配置、层)都通过唯一的哈希值(摘要,Digest)进行标识,而描述符则记录了组件的哈希、大小、媒体类型等元数据,形成组件间的引用关系。由于每个组件的哈希基于其内容计算,且引用关系不存在循环(无环),因此整体构成一个有向无环图。这种结构确保了镜像内容的可验证性 —— 任何组件的修改都会导致其哈希变化,进而影响依赖它的所有上层组件的哈希,实现了内容的完整性校验和追溯。
这一结构是 OCI 镜像实现内容寻址、去重存储和安全验证的基础,使得镜像在传输、存储和分发过程中能够保持一致性和可靠性。
默克尔有向无环图介绍:
2013年以色列学者在bitcointalk提出GHOST协议,引入DAG的概念,最早是作为比特币的交易能力扩容解决方案。
假设当你发布新交易时,那么你的单元会主动同时链接到前面两个有效单元之中,DAG 中的每个新单元,验证并确认其父单元,以及父单元的父单元,慢慢可达创世单元,并将其父单元的哈希包含到自己的单元里面。
随着时间递增,所有交易单元相互连接,形成图状结构,如若要更改数据,那就不仅仅是几个单元数据的问题了,而是整个拓扑图的数据更改。DAG这个模式相比来说,要进行的复杂度更高,更难以被更改,恰巧容器的镜像也巧妙的使用了这个特性,增加内容被篡改的成本
3.1 Properties(属性)
原文:
A descriptor consists of a set of properties encapsulated in key-value fields.
描述符由一组封装在键值对中的属性组成。
The following fields contain the primary properties that constitute a Descriptor:
下面是描述符的核心字段说明:
mediaTypestring 字符型This REQUIRED property contains the media type of the referenced content. Values MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2.
这一必填属性包含了所应用内容的媒体类型。其值必须符合RFC 6838标准(url:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6838 ),包括该标准第 4.2 节中规定的命名要求。
The OCI image specification defines several of its own MIME types for resources defined in the specification.
OCI 镜像规范为该规范中定义的资源制定了若干专属的 MIME 类型。
digeststring 字符型This REQUIRED property is the digest of the targeted content, conforming to the requirements outlined in Digests. Retrieved content SHOULD be verified against this digest when consumed via untrusted sources.
*这一必填属性反映了目标内容的摘要,需符合《摘要(Digests)》部分中规定的要求。当从不可信源获取内容时,应当根据此摘要对内容进行校验。*
sizeint64 整型This REQUIRED property specifies the size, in bytes, of the raw content. This property exists so that a client will have an expected size for the content before processing. If the length of the retrieved content does not match the specified length, the content SHOULD NOT be trusted.
这一必填字段反映了原始内容的字节大小。因为这个字段的存在,所以客户端在处理内容时会得到一个期待的内容大小值。如果获取的内容的大小和期待的内容大小并不匹配,那么此内容就应当认为不可信内容。
urlsarray of strings 字符型数组This OPTIONAL property specifies a list of URIs from which this object MAY be downloaded. Each entry MUST conform to RFC 3986. Entries SHOULD use the
httpandhttpsschemes, as defined in RFC 7230.这是一个可选填的字段,表示的时一组下载指定对象的URL列表,每个条目必须遵循RFC 3986(url:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986)标准。条目**应当**使用 RFC 7230 (url: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-2.7)中定义的 http 和 https 协议方案。
annotationsstring-string map 字符字典型This OPTIONAL property contains arbitrary metadata for this descriptor. This OPTIONAL property MUST use the annotation rules.
这是一个可选填的字段,表示此描述符的任意元数据。当前可选属性必须本规范中的《遵循注释》规则。
datastring 字符型This OPTIONAL property contains an embedded representation of the referenced content. Values MUST conform to the Base 64 encoding, as defined in RFC 4648. The decoded data MUST be identical to the referenced content and SHOULD be verified against the
digestandsizefields by content consumers. See Embedded Content for when this is appropriate.这是一个可选填的字段,包含了所引用内容的内嵌表示。其值必须符合 RFC 4648(url:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4648#section-4) 中定义的 Base64 编码标准。解码后的数据必须与被引用的数据完全一致,内容消费者应该根据摘要(digest)和大小(size)字段对其进行验证。关于嵌入内容部分还请参考本规范《Embedded Content 》章节。
artifactTypestring 字符型This OPTIONAL property contains the type of an artifact when the descriptor points to an artifact. This is the value of the config descriptor
mediaTypewhen the descriptor references an image manifest. If defined, the value MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2, and MAY be registered with IANA.这是一个可选填的字段,当该描述符指向某个制品时,应该包含该制品的类型。当描述符引用镜像清单时,此属性应该被配置为媒体类型。若定义了该属性,其值必须符合 RFC 6838 标准(url:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6838)(包括该标准第 4.2 节中的命名要求),且可在 IANA 进行注册。
Descriptors pointing to application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json SHOULD include the extended field platform, see Image Index Property Descriptions for details.
指向 application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json 的描述符应包含扩展字段 platform,详情参见《镜像索引属性说明》。
3.1.1 Reserved(预留)
Extended Descriptor field additions proposed in other OCI specifications SHOULD first be considered for addition into this specification.
*在其他 OCI 规范中提出的扩展描述符字段新增内容,应首先考虑纳入本规范。*
3.2 Digests(摘要)
The digest property of a Descriptor acts as a content identifier, enabling content addressability. It uniquely identifies content by taking a collision-resistant hash of the bytes. If the digest can be communicated in a secure manner, one can verify content from an insecure source by recalculating the digest independently, ensuring the content has not been modified.
描述符的摘要属性扮演一个内容唯一标识符的角色,支持内容寻址功能。通过对字节数据进行抗碰撞哈希计算来唯一标识内容。如果摘要以更安全的方式进行传递,那么即使从不可信的源获取数据内容,依然可以进行对摘要的内容进行重新计算验证,确保内容没有被篡改。
The value of the digest property is a string consisting of an algorithm portion and an encoded portion. The algorithm specifies the cryptographic hash function and encoding used for the digest; the encoded portion contains the encoded result of the hash function.
摘要内容是一个由算法部分和摘要部分共同组成的字符串内容。算法部分指定了用于生成摘要的加密哈希函数以及编码方式。编码部分包含了哈希部分的编码结果。
A digest string MUST match the following grammar:
一个摘要的字符内容必须符合下面的语法规则:
1 | digest ::= algorithm ":" encoded |
Note that algorithm MAY impose algorithm-specific restriction on the grammar of the encoded portion. See also Registered Algorithms.
Some example digest strings include the following:
注意:
算法可能会对编码部分的语法施加算法限制,另请参考已注册的算法部分内容。
下面是一些摘要内容的例子:
| digest | algorithm | Registered |
|---|---|---|
sha256:6c3c624b58dbbcd3c0dd82b4c53f04194d1247c6eebdaab7c610cf7d66709b3b |
SHA-256 | Yes |
sha512:401b09eab3c013d4ca54922bb802bec8fd5318192b0a75f201d8b372742... |
SHA-512 | Yes |
multihash+base58:QmRZxt2b1FVZPNqd8hsiykDL3TdBDeTSPX9Kv46HmX4Gx8 |
Multihash | No |
sha256+b64u:LCa0a2j_xo_5m0U8HTBBNBNCLXBkg7-g-YpeiGJm564 |
SHA-256 with urlsafe base64 | No |
Please see Registered Algorithms for a list of registered algorithms.
请看已注册算法列表内容。
Implementations SHOULD allow digests with unrecognized algorithms to pass validation if they comply with the above grammar. While sha256 will only use hex encoded digests, separators in algorithm and alphanumerics in encoded are included to allow for extensions. As an example, we can parameterize the encoding and algorithm as multihash+base58:QmRZxt2b1FVZPNqd8hsiykDL3TdBDeTSPX9Kv46HmX4Gx8, which would be considered valid but unregistered by this specification.
如果符合上述语法,实现 SHOULD 允许使用无法识别的算法的 digest 通过验证。虽然 sha256 将仅使用十六进制编码的 digest,但算法中的分隔符和编码中的字母数字都包含在内以允许扩展。例如,我们可以将编码和算法参数化为 multihash+base58:QmRZxt2b1FVZPNqd8hsiykDL3TdBDeTSPX9Kv46HmX4Gx8,这将被视为有效但未被本规范注册。
3.2.1 Verification(校验)
Before consuming content targeted by a descriptor from untrusted sources, the byte content SHOULD be verified against the digest string. Before calculating the digest, the size of the content SHOULD be verified to reduce hash collision space. Heavy processing before calculating a hash SHOULD be avoided. Implementations MAY employ canonicalization of the underlying content to ensure stable content identifiers.
*在从不可信源获取标识符所指向的内容使用之前,应该根据摘要字符串对字节内容进行校验。在计算摘要之前,应该先验证内容的大小,以减少哈希碰撞的可能性。应该避免在计算哈希之前进行大量处理。实现方案可对底层内容做标准化的处理保证内容标识的稳定性。*
3.2.2 Digest calculations(摘要计算)
原文:
A digest is calculated by the following pseudo-code, where H is the selected hash algorithm, identified by string <alg>:
摘要计算的大致伪代码如下所示,H是被选择的其中一种摘要算法,使用字符<alg>表示:
1 | let ID(C) = Descriptor.digest |
Above, we define the content identifier as ID(C), extracted from the Descriptor.digest field. Content C is a string of bytes. Function H returns the hash of C in bytes and is passed to function Encode and prefixed with the algorithm to obtain the digest. The result verified is true if ID(C) is equal to D, confirming that C is the content identified by D. After verification, the following is true:
如上述的伪代码所示,我们从描述符的摘要字段中获取内容,将此内容定义为ID(C)对象,作为内容的身份标识符。内容C是字符串字节数据。函数H返会C的字节形式的哈希值,该哈希值又被传入编码函数Encode做进一步的处理,在结果之前加上算法标识以得到摘要,如果ID(C)和D相等,那么校验的结果即为真,即确认C就是D所标识的内容。进过验证之后,下面的对等关系成立。
1 | D == ID(C) == '<alg>:' + Encode(H(C)) |
The digest is confirmed as the content identifier by independently calculating the digest.
通过独立计算摘要可以确认摘要即为内容的标识符。
3.2.3 Registered algorithms(已注册的算法)
原文:
While the algorithm component of the digest string allows the use of a variety of cryptographic algorithms, compliant implementations SHOULD use SHA-256.
尽管摘要字符串的算法部分使用了多种加密算法,合规的实现应该使用SHA-256。
The following algorithm identifiers are currently defined by this specification:
下面是当前规范定义的算法:
| algorithm identifier | algorithm |
|---|---|
sha256 |
SHA-256 |
sha512 |
SHA-512 |
If a useful algorithm is not included in the above table, it SHOULD be submitted to this specification for registration.
SHA-256(SHA-256算法)
SHA-256 is a collision-resistant hash function, chosen for ubiquity, reasonable size and secure characteristics. Implementations MUST implement SHA-256 digest verification for use in descriptors.
SHA-256(url: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4634#section-4.1)是一种抗碰撞哈希函数,因其普适性,合理的长度以及安全特性而被选用。实现**必须**在描述符中使用SHA-256作为摘要内容的算法实现。
When the algorithm identifier is sha256, the encoded portion MUST match /[a-f0-9]{64}/. Note that [A-F] MUST NOT be used here.
SHA-512(SHA-512算法)
SHA-512 is a collision-resistant hash function which may be more performant than SHA-256 on some CPUs. Implementations MAY implement SHA-512 digest verification for use in descriptors.
When the algorithm identifier is sha512, the encoded portion MUST match /[a-f0-9]{128}/. Note that [A-F] MUST NOT be used here.
当使用SHA-512作为摘要内容的算法时,编码部分必须匹配正则表达式 /[a-f0-9]{128}/。请注意,此处禁止使用 [A-F](大写字母)。
3.3 Embedded Content(内嵌内容)
In many contexts, such as when downloading content over a network, resolving a descriptor to its content has a measurable fixed “roundtrip” latency cost. For large blobs, the fixed cost is usually inconsequential, as the majority of time will be spent actually fetching the content. For very small blobs, the fixed cost can be quite significant.
在大多数场景下,如通过网络下载内容,将描述符解析为其实际对应的内容会产生可量化固定的“往返”延时成本开销。对于大型二进制数据块(blobs)而言,这种固定成本通常无关紧要,因为大部分时间会花费在获取内容的过程中。但是在小型二进制数据块(blobs)传输中,这种固定成本开销会变得非常明显。
Implementations MAY choose to embed small pieces of content directly within a descriptor to avoid roundtrips.
实现方案可以选择将小型内容内嵌在描述符中以避免往返延迟。
Implementations MUST NOT populate the data field in situations where doing so would modify existing content identifiers. For example, a registry MUST NOT arbitrarily populate data fields within uploaded manifests, as that would modify the content identifier of those manifests. In contrast, a client MAY populate the data field before uploading a manifest, because the manifest would not yet have a content identifier in the registry.
实现不能在可能修改内容标识符的情况下填充data字段。如,注册表严禁随意填充已上传清单中的data字段的内容。因为会改变清单的内容标识符。相反地,客户端可以在上传清单之前填充data字段的内容,因为此时该清单的注册表中还尚未拥有内容标识符的内容。
Implementations SHOULD consider portability when deciding whether to embed data, as some providers are known to refuse to accept or parse manifests that exceed a certain size.
实现应该考虑嵌入数据的可移植性,因为已知的部分服务商拒绝解析超过特定大小的清单。
3.4 Examples (例子)
原文:
The following example describes a Manifest with a content identifier of
下面的例子描述了一份带有摘要内容标识符的Manifest清单,内容是:
“sha256:5b0bcabd1ed22e9fb1310cf6c2dec7cdef19f0ad69efa1f392e94a4333501270” and a size of 7682 bytes:
1 | { |
In the following example, the descriptor indicates that the referenced manifest is retrievable from a particular URL:
下面的示例,表示当前描述符所引用Manifest清单的URL地址:
1 | { |
In the following example, the descriptor indicates the type of artifact it is referencing:
下面的示例,表示当前描述符所引用的制品类型:
1 | { |
4 OCI Image Layout Specification(OCI 镜像布局规范)
The OCI Image Layout is the directory structure for OCI content-addressable blobs and location-addressable references (refs).
OCI Image layout 镜像布局是用于存储OCI内容可寻址二进制块(blobs)和可寻址引用(refs)的目录结构。
This layout MAY be used in a variety of different transport mechanisms: archive formats (e.g. tar, zip), shared filesystem environments (e.g. nfs), or networked file fetching (e.g. http, ftp, rsync).
该布局可以用于不同的文件传输机制:归档格式(如tar,zip),共享环境变量(如nfs),或者是文件文件获取(如 http,ftp,rsync)。
Given an image layout and a ref, a tool can create an OCI Runtime Specification bundle by:
给定一个镜像的布局和一个引用,工具可以通过OCI运行时规范(url:https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec/blob/v1.2.0/bundle.md)创建一个bundle:
Following the ref to find a manifest, possibly via an image index
通过引用找到一个Manifest文件,这里可能是通过image-index
Applying the filesystem layers in the specified order
按照指定的顺序使用文件系统层。
Converting the image configuration into an OCI Runtime Specification
config.json将指定的镜像配置转换为OCI运行时规范(url:https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec/blob/v1.2.0/config.md))的config文件(url:https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec/blob/v1.2.0/config.md)
4.1 Content(内容)
The image layout is as follows:
镜像的布局如下:
blobs directory
目录类型
Contains content-addressable blobs
容器可寻址二进制数据块
A blob has no schema and SHOULD be considered opaque
*二进制数据块没有固定的模式或者是架构,应该被视为不透明数据。*
Directory MUST exist and MAY be empty
blobs目录必须存在,即使无内容。
See blobs section
查看下面的
blob章节查看具体细节。
oci-layout file
文件类型
It MUST exist
必须存在
It MUST be a JSON object
内容必须是一个json结构对象
It MUST contain an
imageLayoutVersionfield必须包含
imageLayoutVersion字段See oci-layout file section
查看下面 oci-layout file 章节查看具体细节
It MAY include additional fields
它可能包含其他额外的字段
index.json file
文件类型
It MUST exist
必须存在
It MUST be an image index JSON object.
它必须包含image index Json对象。
See index.json section
详情查看下面的index.json章节
Implementor’s Note: For extensibility and future expansion, additional files may be included in the directory. Implementations should not error when encountering unknown files. A common usage includes the manifest.json file associated with a backwards compatible docker save format.
实现者注意事项:
为满足可拓展性和未来的可拓展需求,当前目录下可能会存在额外的文件。实现者在遇到未知文件时,不应该主动报错。常见的应用场景就是目录中可能包含向后兼容的docker save格式相关的manifest文件。
4.2 Example Layout (布局示例)
原文:
This is an example image layout:
这是一个镜像布局的例子:
1 | $ cd example.com/app/ |
Blobs are named by their contents:
Blobs目录下面的由内容命名:
1 | $ shasum -a 256 ./blobs/sha256/afff3924849e458c5ef237db5f89539274d5e609db5db935ed3959c90f1f2d51 |
4.3 Blobs (binary large object 二进制大对象)
Object names in the
blobssubdirectories are composed of a directory for each hash algorithm, the children of which will contain the actual content.Blobs的子目录中的对象名由每个哈希算法对应的目录构成,这些目录的子项包含实际的内容。
The content of
blobs/<alg>/<encoded>MUST match the digest<alg>:<encoded>(referenced per descriptor). For example, the content ofblobs/sha256/da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709MUST match the digestsha256:da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709.内容的路径
blobs/<alg>/<encoded>**必须**匹配摘要格式<alg>:<encoded>完全匹配(依照描述符的引用)。比如,内容的路径是blobs/sha256/da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709必须要摘要的内容sha256:da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709完全匹配。The character set of the entry name for
<alg>and<encoded>MUST match the respective grammar elements described in descriptor.<alg>和<encoded>的条目名称字符集必须与描述符中所述的相应语法元素一致。The blobs directory MAY contain blobs which are not referenced by any of the refs.
blobs目录中可以包含未被任何引用(refs)所引用的 blob 数据。The blobs directory MAY be missing referenced blobs, in which case the missing blobs SHOULD be fulfilled by an external blob store.
blobs目录中可能缺少被引用的 blob 数据,在此情况下,缺失的 blob 数据应由外部 blob 存储来补充。
4.3.1 Example Blobs(二进制大对象示例)
完整例子,这里不做翻译,具体的可以对照上一篇<<OCI Image Format Specification Part1-物理解剖容器Image>>
1 | $ cat ./blobs/sha256/9b97579de92b1c195b85bb42a11011378ee549b02d7fe9c17bf2a6b35d5cb079 | jq |
4.4 oci-layout file (oci-layout文件)
This JSON object serves as a marker for the base of an Open Container Image Layout and to provide the version of the image-layout in use. The imageLayoutVersion value will align with the OCI Image Specification version at the time changes to the layout are made, and will pin a given version until changes to the image layout are required. This section defines the application/vnd.oci.layout.header.v1+json media type.
该Json对象用作容器开放布局(Open Container Image Layout)的根目录标识,提供了正在使用镜像布局的版本信息。imageLayoutVersion的实际内容与镜像布局发生变更时的OCI镜像规范(OCI Image Specification)保持一致,且会固定成特定的版本,版本信息会一直使用直至进行布局需要修改。这个章节定义了application/vnd.oci.layout.header.v1+json 这一媒体类型。
4.4.1 oci-layout Example(oci-layout文件内容示例)
1 | { |
4.5 index.json file(镜像索引文件)
This REQUIRED file is the entry point for references and descriptors of the image-layout. The image index is a multi-descriptor entry point.
作为镜像布局的引用和描述入口的必填入口文件。image index是一个多描述符的入口。
This index provides an established path (/index.json) to have an entry point for an image-layout and to discover auxiliary descriptors.
索引提供了既定路径(/index.json),作为镜像布局的入口,并用于发现辅助描述符。
No semantic restriction is given for the “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name” annotation of descriptors.
对于 “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name”的注释没有任何语义限制。
In general the
mediaTypeof each descriptor object in themanifestsfield will be eitherapplication/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+jsonorapplication/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json.通常情况下,manifest文件中的
mediaType字段中的每一个描述符对象要么是application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json要么是application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+jsonFuture versions of the spec MAY use a different mediatype (i.e. a new versioned format).
未来版本的规范可能会使用一个不同的媒体类型(在一个新版本中的格式)
An encountered
mediaTypethat is unknown MUST NOT generate an error.遇到未定义未知的媒体类型必须产生一个错误。
Implementor’s Note: A common use case of descriptors with a “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name” annotation is representing a “tag” for a container image. For example, an image may have a tag for different versions or builds of the software. In the wild you often see “tags” like “v1.0.0-vendor.0”, “2.0.0-debug”, etc. Those tags will often be represented in an image-layout repository with matching “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name” annotations like “v1.0.0-vendor.0”, “2.0.0-debug”, etc.
带有 “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name” 注解的描述符的一个常见用例是表示容器镜像的 “标签(tag)”。例如,一个镜像可能为软件的不同版本或构建版本设置标签。在实际场景中,你经常会看到诸如 “v1.0.0-vendor.0”、“2.0.0-debug” 等 “标签”。这些标签通常会在镜像布局(imagelayout)仓库中通过匹配的 “org.opencontainers.image.ref.name” 注解来表示,例如 “v1.0.0-vendor.0”、“2.0.0-debug” 等。
4.5.1 Index Example(镜像索引文件示例)
1 | { |
This illustrates an index that provides two named references and an auxiliary mediatype for this image layout.
这是一个索引,它为镜像布局提供了两个命名的索引和一个辅助媒体类型。
The first named reference (stable-release) points to another index that might contain multiple references with distinct platforms and annotations. Note that the org.opencontainers.image.ref.name annotation SHOULD only be considered valid when on descriptors on index.json.
第一个命名引用(stable-release)指向了另外一个索引,该索引可能包含多个不同平台和注释信息的引用。仅当org.opencontainers.image.ref.name annotation注释存在于index.json描述符中才视为有效。
The second named reference (v1.0) points to a manifest that is specific to the linux/ppc64le platform.
第二个命名引用(V1.0)指向了一个linux/ppc64l平台的manifest
5 OCI Image Manifest Specification
There are three main goals of the Image Manifest Specification. The first goal is content-addressable images, by supporting an image model where the image’s configuration can be hashed to generate a unique ID for the image and its components. The second goal is to allow multi-architecture images, through a “fat manifest” which references image manifests for platform-specific versions of an image. In OCI, this is codified in an image index. The third goal is to be translatable to the OCI Runtime Specification.
This section defines the application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json media type. For the media type(s) that this is compatible with see the matrix.
镜像清单规范有三个目标。
- 第一个目标是实现内容可寻址镜像,通过支持一种镜像模型,该模型中,镜像的配置可通过哈希计算得到一个唯一的标识符UID。
- 第二个目标是支持多架构镜像,借助”fat manifest”胖清单实现,该清单会引用特定版本的镜像清单,在OCI中,通过镜像索引进行规范化定义。
- 第三个目标是能够转换为OCI容器运行时规范(OCI Runtime Specification)(url:https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec )
本章节定义了application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json的媒体类型。关于与之兼容的媒体类型,参考1.5 Compatibility Matrix(兼容性矩阵)章节。
5.1 Image Manifest(镜像清单)
Unlike the image index, which contains information about a set of images that can span a variety of architectures and operating systems, an image manifest provides a configuration and set of layers for a single container image for a specific architecture and operating system.
与镜像索引不同,镜像索引包含一组可横跨多种架构和操作系统信息,镜像清单则是为指定的架构和操作系统提供配置和一组与之相关的容器镜像层。
5.2 Image Manifest Property Descriptions(镜像清单属性描述符)
schemaVersionint 整型This REQUIRED property specifies the image manifest schema version. For this version of the specification, this MUST be
2to ensure backward compatibility with older versions of Docker. The value of this field will not change. This field MAY be removed in a future version of the specification.这个必填字段指定了镜像清单的Schema的版本。当前版本指定该字段的内容只能是2。确保与旧版本的Docker向后兼容,此字段的值不会发生变化。未来新版本的规范可能会移除当前字段
mediaTypestring 字符型This property SHOULD be used and remain compatible with earlier versions of this specification and with other similar external formats. When used, this field MUST contain the media type
application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json. This field usage differs from the descriptor use ofmediaType.该属性应被使用,且需与本规范的早期版本以及其他类似的外部格式保持兼容。当使用此字段时,其必须包含媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json。此字段的用法与描述符中mediaType的用法不同。artifactTypestring 字符型This OPTIONAL property contains the type of an artifact when the manifest is used for an artifact. This MUST be set when
config.mediaTypeis set to the empty value. If defined, the value MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2, and MAY be registered with IANA. Implementations storing or copying image manifests MUST NOT error on encountering anartifactTypethat is unknown to the implementation.*这个可选属性在清单用于制品(artifact)时包含该制品的类型。当
config.mediaType被设置为空值时,此字段必须被设置。若此字段已定义,其值必须符合 RFC 6838 标准(包括该标准第 4.2 节中的命名要求),且可以在 IANA 进行注册。存储或复制镜像清单的实现方案在遇到自身不识别的artifactType时,不得报错。*configdescriptor 描述符对象This REQUIRED property references a configuration object for a container, by digest. Beyond the descriptor requirements, the value has the following additional restrictions:
这个必填属性通过摘要引用容器的配置对象。除描述符的要求外,该值还需满足以下额外限制:
mediaTypestring 字符型This descriptor property has additional restrictions for
config.这个必填属性通过摘要引用容器的配置对象。除描述符的要求外,该值还需满足以下额外限制:
Implementations MUST NOT attempt to parse the referenced content if this media type is unknown and instead consider the referenced content as arbitrary binary data (e.g.: as
application/octet-stream).如果此媒体类型未知,实现方案不得尝试解析所引用的内容,而应将引用的内容视为任意二进制数据(例如:当作
application/octet-stream类型处理)。Implementations storing or copying image manifests MUST NOT error on encountering a value that is unknown to the implementation.
*存储或复制镜像清单的实现方案在遇到自身不识别的值时,不得报错。*
Implementations MUST support at least the following media types:
实现方案必须至少支持以下媒体类型:
Manifests for container images concerned with portability SHOULD use one of the above media types. Manifests for artifacts concerned with portability SHOULD use
config.mediaTypeas described in Guidelines for Artifact Usage.关注可移植性的容器镜像清单应使用上述媒体类型之一。关注可移植性的工件清单应按照《制品使用指南》(Guidelines for Artifact Usage)中的描述使用
config.mediaType。If the manifest uses a different media type than the above, it MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2, and MAY be registered with IANA.
如果清单使用的媒体类型与上述类型不同,则其必须符合 RFC 6838 标准,且可以在 IANA 进行注册。
To set an effectively null or empty config and maintain portability see the guidance for an empty descriptor below, and
DescriptorEmptyJSONof the reference code.要设置一个实际上为空的配置并保持可移植性,请参见下文关于空描述符的指南以及参考代码中的
DescriptorEmptyJSON。If this image manifest will be “runnable” by a runtime of some kind, it is strongly recommended to ensure it includes enough data to be unique (such as the
rootfsanddiff_idsincluded inapplication/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json) so that it has a uniqueImageID.如果此镜像清单将能通过某种运行时环境 “运行”,强烈建议确保其包含足够的数据以保证唯一性(例如
application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json中包含的rootfs和diff_ids),这样它才能拥有唯一的镜像 ID(ImageID)。layersarray of objects 对象数组Each item in the array MUST be a descriptor. For portability,
layersSHOULD have at least one entry. See the guidance for an empty descriptor below, andDescriptorEmptyJSONof the reference code.*数组中的每个元素必须是一个描述符。为保证可移植性,层(layers)应至少包含一个条目。请参见下文关于空描述符的指南以及参考代码中的
DescriptorEmptyJSON。*When the
config.mediaTypeis set toapplication/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json, the following additional restrictions apply:当
config.mediaType被设置为application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json时,需适用以下额外限制:The array MUST have the base layer at index 0.
该数组必须将基础层(base layer)放在索引 0 的位置。
Subsequent layers MUST then follow in stack order (i.e. from
layers[0]tolayers[len(layers)-1]).后续的层(Subsequent layers)必须按照堆叠顺序排列,即从数组的索引 0 位置(layers [0])依次排列到数组的最后一个索引位置(layers [len (layers)-1])
The final filesystem layout MUST match the result of applying the layers to an empty directory.
最终的文件系统布局必须与将各层应用于空目录后得到的结果一致。
The ownership, mode, and other attributes of the initial empty directory are unspecified.
初始空目录的所有权、权限模式及其他属性为未指明状态。
Beyond the descriptor requirements, the value has the following additional restrictions:
除描述符的要求外,该值还需满足以下额外限制:
mediaTypestring 字符型This descriptor property has additional restrictions for
layers[]. Implementations MUST support at least the following media types:该描述符属性对
layers[](层数组)有额外限制。实现方案必须至少支持以下媒体类型:application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzipapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar(deprecation notice)application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip(deprecation notice)
Manifests concerned with portability SHOULD use one of the above media types. Entries in this field will frequently use the
+gziptypes.关注可移植性的清单应使用上述媒体类型之一。此字段中的条目通常会使用带
+gzip的类型。Implementations SHOULD also support the following media types:
实现方案还应支持以下媒体类型:
Implementations storing or copying image manifests MUST NOT error on encountering a
mediaTypethat is unknown to the implementation.*存储或复制镜像清单的实现方案在遇到自身不识别的
mediaType时,不得报错。*If the manifest uses a different media type than the above, it MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2, and MAY be registered with IANA.
如果清单使用的媒体类型与上述类型不同,则其必须符合 RFC 6838 标准,且可以在 IANA 进行注册。
See Guidelines for Artifact Usage for other uses of the
layers.参见《制品使用指南》了解层(layers)的其他用途。
subjectdescriptor 描述符对象This OPTIONAL property specifies a descriptor of another manifest. This value defines a weak association to a separate Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, and is used by the
referrersAPI to include this manifest in the list of responses for the subject digest.此可选属性指定了另一个清单的描述符。该值定义了与独立的默克尔有向无环图(Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph,简称 Merkle DAG)结构的弱关联,且被引用者 API(referrers API)用于将此清单纳入主题摘要的响应列表中。
annotationsstring-string map 字典类型This OPTIONAL property contains arbitrary metadata for the image manifest. This OPTIONAL property MUST use the annotation rules.
此可选属性包含镜像清单的任意元数据。该可选属性必须遵循注解规则。
See Pre-Defined Annotation Keys.
参见预定义注解键。
5.3 Example Image Manifest (镜像清单示例)
Example showing an image manifest:
下面是一份镜像清单的示例:
1 | { |
5.4 Guidance for an Empty Descriptor (空描述符指导)
Implementers note: The following is considered GUIDANCE for portability.
实现者说明:以下内容被视为可移植性方面的指导建议。
Parts of the spec necessitate including a descriptor to a blob where some implementations of artifacts do not have associated content. While an empty blob (size of 0) may be preferable, practice has shown that not to be ubiquitously supported. The media type application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json (MediaTypeEmptyJSON) has been specified for a descriptor that has no content for the implementation. The blob payload is the most minimal content that is still a valid JSON object: {} (size of 2). The blob digest of {} is sha256:44136fa355b3678a1146ad16f7e8649e94fb4fc21fe77e8310c060f61caaff8a. The data field is optional, and if included is the base64 encoding of {}: e30=.
规范中的部分内容要求包含指向blobs的描述符,而某些制品实现可能不存在关联内容。虽然blob(大小为0)可能更理想,但是实际上并未得到广泛的支持。因为,规范中定了媒体类型application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json (MediaTypeEmptyJSON),用于表示实现中可能无内容的描述。该内容依旧属于有效的Json对象的最小内容:{}(大小为2)。{}的blob摘要是sha256:44136fa355b3678a1146ad16f7e8649e94fb4fc21fe77e8310c060f61caaff8a。data字段是可选字段,若包含此字段,{}的值转成base64编码是:e30=
The resulting descriptor shown here is also defined in reference code as DescriptorEmptyJSON:
此处所示的最终描述符在参考代码中也被定义为 DescriptorEmptyJSON:
1 | { |
5.5 Guidelines for Artifact Usage(制品使用指导)
Content other than OCI container images MAY be packaged using the image manifest. When this is done, the config.mediaType value MUST be set to a value specific to the artifact type or the empty value. If the config.mediaType is set to the empty value, the artifactType MUST be defined. If the artifact does not need layers, a single layer SHOULD be included with a non-zero size. The suggested content for an unused layers array is the empty descriptor.
*非 OCI 容器镜像的内容可以使用镜像清单(image manifest)进行打包。在此情况下,config.mediaType 的值必须设置为特定于制品类型的值或空值。若 config.mediaType 被设置为空值,则 artifactType必须被定义。如果该制品不需要层(layers),则应包含一个具有非零大小的层。对于未使用的层数组(layers array),建议的内容为空描述符(empty descriptor)。*
The design of the artifact depends on what content is being packaged with the artifact. The decision tree below and the associated examples MAY be used to design new artifacts:
制品的设计取决于该制品所打包的内容。以下决策树及相关示例可用于设计新制品:
Does the artifact consist of at least one file or blob? If yes, continue to 2. If no, specify the
artifactType, and set theconfigand a singlelayerselement to the empty descriptor value. Here is an example of this with annotations included:该制品是否包含至少一个文件或 blob 数据?若是,请继续至第 2 点。若否,则需指定
artifactType,并将配置(config)和单个层(layers)元素设置为空描述符(empty descriptor)值。以下是包含注解的示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21{
"schemaVersion": 2,
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json",
"artifactType": "application/vnd.example+type",
"config": {
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json",
"digest": "sha256:44136fa355b3678a1146ad16f7e8649e94fb4fc21fe77e8310c060f61caaff8a",
"size": 2
},
"layers": [
{
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json",
"digest": "sha256:44136fa355b3678a1146ad16f7e8649e94fb4fc21fe77e8310c060f61caaff8a",
"size": 2
}
],
"annotations": {
"oci.opencontainers.image.created": "2023-01-02T03:04:05Z",
"com.example.data": "payload"
}
}Does the artifact have additional JSON formatted metadata as configuration? If yes, continue to 3. If no, specify the
artifactType, include the artifact in thelayers, and setconfigto the empty descriptor value. Here is an example of this with a single layer:该制品是否包含额外的 JSON 格式元数据作为配置?若是,请继续至第 3 点。若否,则需指定
artifactType,将制品包含在层(layers)中,并将配置(config)设置为空描述符(empty descriptor)值。以下是包含单个层的示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17{
"schemaVersion": 2,
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json",
"artifactType": "application/vnd.example+type",
"config": {
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.empty.v1+json",
"digest": "sha256:44136fa355b3678a1146ad16f7e8649e94fb4fc21fe77e8310c060f61caaff8a",
"size": 2
},
"layers": [
{
"mediaType": "application/vnd.example+type",
"digest": "sha256:e258d248fda94c63753607f7c4494ee0fcbe92f1a76bfdac795c9d84101eb317",
"size": 1234
}
]
}For artifacts with a config blob, specify the
artifactTypeto a common value for your artifact tooling, specify theconfigwith the metadata for this artifact, and include the artifact in thelayers. Here is an example of this:对于包含配置 blob 的制品,需将
artifactType指定为适用于制品工具的通用值,将配置(config)指定为该制品的元数据,并将制品包含在层(layers)中。以下是相关示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17{
"schemaVersion": 2,
"mediaType": "application/vnd.oci.image.manifest.v1+json",
"artifactType": "application/vnd.example+type",
"config": {
"mediaType": "application/vnd.example.config.v1+json",
"digest": "sha256:5891b5b522d5df086d0ff0b110fbd9d21bb4fc7163af34d08286a2e846f6be03",
"size": 123
},
"layers": [
{
"mediaType": "application/vnd.example.data.v1.tar+gzip",
"digest": "sha256:e258d248fda94c63753607f7c4494ee0fcbe92f1a76bfdac795c9d84101eb317",
"size": 1234
}
]
}
Implementers note: artifacts have historically been created without an artifactType field, and tooling to work with artifacts should fallback to the config.mediaType value.
实现者说明:在历史实践中,制品的创建曾未包含 artifactType 字段,因此处理制品的工具应退而使用 config.mediaType 的值。
6 OCI Image Index Specification(OCI镜像规范索引规范)
The image index is a higher-level manifest which points to specific image manifests, ideal for one or more platforms. While the use of an image index is OPTIONAL for image providers, image consumers SHOULD be prepared to process them.
镜像索引是一个更高维度的清单,它指向特定的镜像清单,适合用于一个或者多个平台的场景。对于镜像提供者而言,镜像索引的使用是可选的,但是镜像的消费者应做好处理镜像索引的准备。
This section defines the application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json media type.
本节定义了 application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json 媒体类型。
For the media type(s) that this document is compatible with, see the matrix.
关于本文档兼容的媒体类型,请参见上面的矩阵表。
6.1 Image Index Property Descriptions(镜像索引属性描述符)
schemaVersionint 整型This REQUIRED property specifies the image manifest schema version. For this version of the specification, this MUST be
2to ensure backward compatibility with older versions of Docker. The value of this field will not change. This field MAY be removed in a future version of the specification.这一必填属性指定了镜像清单的Schema版本。对于本版本的规范,其内容必须是
2,以确保与旧版本的Docker向后兼容。当前字段不会发生变更,未来的版本演进可能会移除当前字段。mediaTypestring 字符型This property SHOULD be used and remain compatible with earlier versions of this specification and with other similar external formats. When used, this field MUST contain the media type
application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json. This field usage differs from the descriptor use ofmediaType.此属性应被使用,且需与本规范的早期版本及其他类似外部格式保持兼容。使用时,此字段必须包含媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json,此字段的用法与描述符中的mediaType用法不同。artifactTypestring 字符型This OPTIONAL property contains the type of an artifact when the manifest is used for an artifact. If defined, the value MUST comply with RFC 6838, including the naming requirements in its section 4.2, and MAY be registered with IANA.
这一可选属性在清单用于制品时包含制品的类型。若定义该属性,其值必须符合 RFC 6838 标准(包括该标准第 4.2 节中的命名要求),且可向 IANA 注册。
manifestsarray of objects 数组对象This REQUIRED property contains a list of manifests for specific platforms. While this property MUST be present, the size of the array MAY be zero.
这一必填属性包含特定平台的清单列表。尽管该属性必须存在,但数组的大小可以为零。
Each object in
manifestsincludes a set of descriptor properties with the following additional properties and restrictions:清单数组(manifests)中的每个对象均包含一组描述符属性,并附加以下属性及限制条件:
mediaTypestring 字符型This descriptor property has additional restrictions for
manifests. Implementations MUST support at least the following media types:此描述符属性对清单有额外限制。实现必须支持至少以下媒体类型:
Also, implementations SHOULD support the following media types:
同时,实现应该支持下列的媒体类型:
application/vnd.oci.image.index.v1+json(nested index)
Image indexes concerned with portability SHOULD use one of the above media types. Future versions of the spec MAY use a different mediatype (i.e. a new versioned format). An encountered
mediaTypethat is unknown to the implementation MUST NOT generate an error.*关注可移植性的镜像索引应使用上述媒体类型之一。本规范的未来版本可能会使用不同的媒体类型(即新的版本化格式)。若实现中遇到未知的媒体类型,不得产生错误。*
platformobject 对象类型This OPTIONAL property describes the minimum runtime requirements of the image. This property SHOULD be present if its target is platform-specific.
这一可选属性描述了镜像的最低运行时要求。若其目标为特定平台,该属性应存在。
architecturestring 字符型This REQUIRED property specifies the CPU architecture. Image indexes SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand, values listed in the Go Language document for
GOARCH.这一必填属性指定了 CPU 架构。镜像索引应使用且实现应理解 Go 语言文档中为
GOARCH列出的值。osstring 字符型This REQUIRED property specifies the operating system. Image indexes SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand, values listed in the Go Language document for
GOOS.这一必填属性指定了操作系统。镜像索引应使用且实现应理解 Go 语言文档中为
GOOS列出的值。os.versionstring 字符型This OPTIONAL property specifies the version of the operating system targeted by the referenced blob. Implementations MAY refuse to use manifests where
os.versionis not known to work with the host OS version. Valid values are implementation-defined. e.g.10.0.14393.1066onwindows.这一可选属性指定了被引用 blob 所针对的操作系统版本。对于
os.version未知是否能与主机操作系统版本兼容的清单,实现工具可拒绝使用。其有效值由实现方式定义,例如在 Windows 系统上可设为 10.0.14393.1066。os.featuresarray of strings 字符型数组This OPTIONAL property specifies an array of strings, each specifying a mandatory OS feature. When
osiswindows, image indexes SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand the following values:这一可选属性指定了一个字符串数组,其中每个字符串均表示一项必需的操作系统功能。当操作系统(os)为 Windows 时,镜像索引应使用且实现工具应理解以下值:
win32k: image requireswin32k.syson the host (Note:win32k.sysis missing on Nano Server)win32k:镜像要求主机上存在 win32k.sys(注:Nano Server 中不包含 win32k.sys)
When
osis notwindows, values are implementation-defined and SHOULD be submitted to this specification for standardization.当操作系统(os)非 Windows 时,其值由实现方式定义,且应提交至本规范以进行标准化。
variantstring 字符型This OPTIONAL property specifies the variant of the CPU. Image indexes SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand,
variantvalues listed in the Platform Variants table.这一可选属性指定了 CPU 的变体。镜像索引应使用且实现工具应理解《平台变体表》中列出的变体值。
featuresarray of strings 字符数组This property is RESERVED for future versions of the specification.
该属性为规范的未来版本*预留。*
If multiple manifests match a client or runtime’s requirements, the first matching entry SHOULD be used.
*如果多个清单与客户端或运行时的要求相匹配,应使用第一个匹配项。*
subjectdescriptor ]描述符对象This OPTIONAL property specifies a descriptor of another manifest. This value defines a weak association to a separate Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, and is used by the
referrersAPI to include this manifest in the list of responses for the subject digest.这一可选属性指定了另一个清单的描述符。该值定义了与独立的默克尔有向无环图(Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph,DAG)结构的弱关联,且被引用者 API 用于将此清单纳入主题摘要的响应列表中。
annotationsstring-string map 字典类型This OPTIONAL property contains arbitrary metadata for the image index. This OPTIONAL property MUST use the annotation rules.
这一可选属性包含镜像索引的任意元数据。此可选属性必须遵循注释规则。
See Pre-Defined Annotation Keys.
参见预定义注释键。
6.2 Platform Variants (平台变体)
When the variant of the CPU is not listed in the table, values are implementation-defined and SHOULD be submitted to this specification for standardization. These values SHOULD match (or be similar to) their analog listed in the Go Language document.
当 CPU 变体未在表格中列出时,其值由实现方式定义,且应提交至本规范以进行标准化。这些值应与 Go 语言文档中列出的对应项一致(或相似)。
| ISA/ABI | architecture |
variant |
Go analog |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARM 32-bit | arm |
v6, v7, v8 |
GOARM |
| ARM 64-bit | arm64 |
v8, v8.1, … |
GOARM64 |
| POWER8+ | ppc64le |
power8, power9, … |
GOPPC64 |
| RISC-V | riscv64 |
rva20u64, … |
GORISCV64 |
| x86-64 | amd64 |
v1, v2, v3, … |
GOAMD64 |
6.3 Example Image Index(镜像索引示例)
Example showing a simple image index pointing to image manifests for two platforms:
示例:展示一个指向两个平台的镜像清单的简单镜像索引:
1 | { |
6.4 Example Image Index with multiple media types(多媒体类型的镜像索引示例)
Example showing an image index pointing to manifests with multiple media types:
示例:展示一个指向多种媒体类型清单的镜像索引:
1 | { |
7 Image Layer Filesystem Changeset (镜像层文件系统变更集)
This document describes how to serialize a filesystem and filesystem changes like removed files into a blob called a layer. One or more layers are applied on top of each other to create a complete filesystem. This document will use a concrete example to illustrate how to create and consume these filesystem layers.
本文档描述了如何将文件系统及文件系统变更(如已删除的文件)序列化为一个名为 “层”(layer)的二进制大对象(blob)。一个或多个层会逐层叠加,以构建完整的文件系统。本文档将通过具体示例说明如何创建和使用这些文件系统层。
This section defines the application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar, application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip, application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+zstd, application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar, application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip, and application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd media types.
本节定义了以下媒体类型:application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar、application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip、application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+zstd、application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar、application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip 以及 application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd(原文末尾 “nondistributab” 疑似拼写错误,此处根据上下文补全为 “nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd”)。
7.1 +gzip Media Types (+gzip媒体类型)
The media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gziprepresents anapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarpayload which has been compressed with gzip.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip表示经过 gzip 压缩的application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar有效载荷。The media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gziprepresents anapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tarpayload (deprecation notice) which has been compressed with gzip.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip表示经过 gzip 压缩的application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar有效载荷(弃用通知)(原文中 “application/vnd.oci.i payload” 存在拼写不完整,根据上下文补全为标准媒体类型application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar)。
7.2 +zstd Media Types(+zstd 媒体类型)
The media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+zstdrepresents anapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarpayload which has been compressed with zstd.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+zstd表示经过 zstd 压缩的application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar有效载荷。The media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstdrepresents anapplication/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tarpayload (deprecation notice) which has been compressed with zstd.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd表示经过 zstd 压缩的application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar有效载荷(弃用通知)(原文中 “application/vnd.oci.i payload” 存在拼写不完整,根据上下文补全为标准媒体类型application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar)。
7.3 Distributable Format(分发格式)
Layer Changesets for the media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarMUST be packaged in tar archive.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar对应的层变更集必须打包为 tar 归档文件。Layer Changesets for the media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarMUST NOT include duplicate entries for file paths in the resulting tar archive.媒体类型
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar对应的层变更集在生成的 tar 归档文件中不得包含文件路径的重复条目。
7.4 Change Types (变更类型)
Types of changes that can occur in a changeset are:
变更集中可能出现的变更类型包括:
Additions
新增
Modifications
修改
Removals
删除
Additions and Modifications are represented the same in the changeset tar archive.
在变更集 tar 归档文件中,新增(Additions)和修改(Modifications)的表示方式相同。
Removals are represented using “whiteout“ file entries (See Representing Changes).
删除操作通过 “空白文件条目”(whiteout file entries)表示(参见《变更的表示方式》)。
7.4.1 File Types(文件类型)
Throughout this document section, the use of word “files” or “entries” includes the following, where supported:
在本文档的本节中,“文件”(files)或 “条目”(entries)一词的使用涵盖以下内容(在支持的情况下):
- regular files (常规文件)
- directories (目录)
- sockets*(套接字)*
- symbolic links(软链接)
- block devices*(块设备)*
- character devices*(字符设备)*
- FIFOs (管道 ps:用于进程间通信,允许无关联的进程通过读写该文件进行数据交换。)
7.4.2 File Attributes(文件属性)
Where supported, MUST include file attributes for Additions and Modifications include:
在支持的情况下,新增(Additions)和修改(Modifications)必须包含的文件属性包括:
Modification Time (
mtime)(文件最后一次的修改时间)User ID (uid)(系统中的用户ID)
User Name (
uname) should be ignored on platforms that support User ID (uid)在支持用户 ID(uid)的平台上,用户名(uname)应被忽略。
Group ID (gid)(系统中用户所归属的组的ID)
Group Name (
gname) should be ignored on platforms that support Group ID (gid)在支持组 ID(gid)的平台上,组名(gname)应被忽略。
Mode (
mode)(权限模式)Extended Attributes (
xattrs) (扩展属性)Symlink reference (
linkname+ symbolic link type) (符号链接引用(链接名 + 符号链接类型)Hardlink reference (
linkname)(硬链接引用(链接名))
Sparse files SHOULD NOT be used because they lack consistent support across tar implementations.
不应使用稀疏文件,因为不同的 tar 实现对稀疏文件的支持并不一致。
译者注:
稀疏文档(Sparse File)是一种通过元数据标记空数据块以节省磁盘空间的计算机文件类型,其逻辑大小大于实际物理存储空间。
7.4.3 Hardlinks(硬链接)
Hardlinks are a POSIX concept for having one or more directory entries for the same file on the same device.
硬链接是一种 POSIX 概念,指在同一设备上为同一个文件创建一个或多个目录条目。
Not all filesystems support hardlinks (e.g. FAT).
并非所有文件系统都支持硬链接(例如 FAT 文件系统)。
Hardlinks are possible with all file types except
directories.硬链接可用于所有文件类型,但目录除外。
Non-directory files are considered “hardlinked” when their link count is greater than 1.
当非目录文件的链接计数大于 1 时,它们会被视为 “硬链接文件”。
Hardlinked files are on a same device (i.e. comparing Major:Minor pair) and have the same inode.
硬链接文件位于同一设备上(即通过主设备号:次设备号对进行比较),且具有相同的索引节点(inode)。
The corresponding files that share the link with the > 1 linkcount may be outside the directory that the changeset is being produced from, in which case the
linknameis not recorded in the changeset.与链接计数大于 1 的文件共享链接的对应文件,可能位于生成变更集的目录之外,在这种情况下,链接名不会记录在变更集中。
Union filesystem implementations may have limited or no support for hardlinks, particularly when a change is made to a hardlinked file or a hardlink is created to a file in a lower filesystem. (See the overlay specification for more details.)
联合文件系统(Union filesystem)的实现对硬链接的支持可能有限,甚至完全不支持,尤其是当对硬链接文件进行修改,或者为低层文件系统中的文件创建硬链接时。(更多细节请参见覆盖层规范。)
Extracting a layer with hardlink references to files outside of the layer may fail.
提取包含指向层外文件的硬链接引用的层时,可能会失败。
Hardlinks are stored in a tar archive with type of a
1char, per the GNU Basic Tar Format and libarchive tar(5).根据 GNU 基本 tar 格式和 libarchive 的 tar (5) 规范,硬链接在 tar 归档中以 1 个字符的类型标识进行存储。
While approaches to deriving new or changed hardlinks may vary, a possible approach is:
尽管推导新增或已更改硬链接的方法可能各不相同,但一种可行的方法是:
1 | SET LinkMap to map[< Major:Minor String >]map[< inode integer >]< path string > |
With this approach, the link map and links names of a directory could be compared against that of another directory to derive additions and changes to hardlinks.
通过这种方法,可以将一个目录的链接映射和链接名称与另一个目录的进行比较,从而推导出硬链接的新增和变更情况。
7.4.4 Platform-specific attributes(平台特定属性)
Implementations on Windows MUST support these additional attributes, encoded in PAX vendor extensions as follows:
Windows 平台上的实现必须支持这些额外属性,它们通过 PAX 供应商扩展按如下方式进行编码:
Windows file attributes (
MSWINDOWS.fileattr)Windows 文件属性(MSWINDOWS.fileattr)
Security descriptor (
MSWINDOWS.rawsd): base64-encoded self-relative binary security descriptor安全描述符(MSWINDOWS.rawsd):经 base64 编码的自相对二进制安全描述符
Mount points (
MSWINDOWS.mountpoint): if present on a directory symbolic link, then the link should be created as a directory junction挂载点(MSWINDOWS.mountpoint):如果存在于目录符号链接中,则该链接应创建为目录连接点(directory junction)。
Creation time (
LIBARCHIVE.creationtime)创建时间(LIBARCHIVE.creationtime)
7.5 Creating (创建)
7.5.1 Initial Root Filesystem (初始化根目录文件系统)
The initial root filesystem is the base or parent layer.
初始根文件系统是基础层或父层。
For this example, an image root filesystem has an initial state as an empty directory. The name of the directory is not relevant to the layer itself, only for the purpose of producing comparisons.
在此示例中,镜像根文件系统的初始状态为一个空目录。该目录的名称与层本身无关,仅用于生成比较结果。
Here is an initial empty directory structure for a changeset, with a unique directory name rootfs-c9d-v1.
以下是变更集的初始空目录结构,其唯一目录名称为 rootfs-c9d-v1。
1 | rootfs-c9d-v1/ |
7.5.2 Populate Initial Filesystem(填充初始化文件系统)
Files and directories are then created:
文件和目录即将被创建:
1 | rootfs-c9d-v1/ |
The rootfs-c9d-v1 directory is then created as a plain tar archive with relative path to rootfs-c9d-v1. Entries for the following files:
随后,rootfs-c9d-v1 目录被创建为一个普通的 tar 归档文件,其路径相对于 rootfs-c9d-v1的。包含以下文件的条目:
1 | ./ |
7.5.3 Populate a Comparison Filesystem (填充一个比较文件系统)
Create a new directory and initialize it with a copy or snapshot of the prior root filesystem. Example commands that can preserve file attributes to make this copy are:
创建一个新目录,并使用先前根文件系统的副本或快照对其进行初始化。可用于执行此复制操作且能保留文件属性的示例命令如下:
- cp(1):
cp -a rootfs-c9d-v1/ rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ - rsync(1):
rsync -aHAX rootfs-c9d-v1/ rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ - tar(1):
mkdir rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 && tar --acls --xattrs -C rootfs-c9d-v1/ -c . | tar -C rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ --acls --xattrs -x(including--selinuxwhere supported)
Any changes to the snapshot MUST NOT change or affect the directory it was copied from.
对快照的任何更改都不得改变或影响其复制来源的目录。
For example rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 is an identical snapshot of rootfs-c9d-v1. In this way rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 is prepared for updates and alterations.
例如,在 /etc/my-app.d 目录下添加一个包含默认配置文件的目录,同时删除现有的配置文件。此外,对 ./bin/my-app-tools 二进制文件进行修改(更改属性或文件内容),以适配配置布局的变更。
Implementor’s Note: a copy-on-write or union filesystem can efficiently make directory snapshots
实现者说明:写时复制(copy-on-write)或联合文件系统(union filesystem)可高效创建目录快照。
Initial layout of the snapshot:
初始化的文件布局快照:
1 | rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ |
See Change Types for more details on changes.
查看6.7章节获取更多细节。
For example, add a directory at /etc/my-app.d containing a default config file, removing the existing config file. Also a change (in attribute or file content) to ./bin/my-app-tools binary to handle the config layout change.
例如,在 /etc/my-app.d 目录下添加一个包含默认配置文件的目录,同时删除现有的配置文件。此外,对 ./bin/my-app-tools 二进制文件进行修改(更改属性或文件内容),以适配配置布局的变更。
Following these changes, the representation of the rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 directory:
完成这些更改后,rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 目录的呈现形式如下:
1 | rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ |
7.5.4 Determining Changes(确定变更)
When two directories are compared, the relative root is the top-level directory. The directories are compared, looking for files that have been added, modified, or removed.
当对两个目录进行比较时,相对根目录为顶层目录。通过比较这些目录,可找出已新增、修改或删除的文件。
For this example, rootfs-c9d-v1/ and rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ are recursively compared, each as relative root path.
在此示例中,rootfs-c9d-v1/ 和 rootfs-c9d-v1.s1/ 会以各自作为相对根路径进行递归比较。
The following changeset is found:
变更集合的细节如下所示:
1 | Added: /etc/my-app.d/ |
This reflects the removal of /etc/my-app-config and creation of a file and directory at /etc/my-app.d/default.cfg. /bin/my-app-tools has also been replaced with an updated version.
当前反映了 /etc/my-app-config 的删除,以及在 /etc/my-app.d/default.cfg 处文件和目录的创建。/bin/my-app-tools 也已被更新版本替换。
7.5.5 Representing Changes(变更呈现)
A tar archive is then created which contains only this changeset:
接着上一步随后会创建一个仅包含此变更集的 tar 归档文件:
Added and modified files and directories in their entirety
完整的新增及修改的文件和目录
Deleted files or directories marked with a whiteout file
用空白文件标记的已删除文件或目录
The resulting tar archive for rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 has the following entries:
针对 rootfs-c9d-v1.s1 生成的 tar 归档文件包含以下条目:
1 | ./etc/my-app.d/ |
To signify that the resource ./etc/my-app-config MUST be removed when the changeset is applied, the basename of the entry is prefixed with .wh..
为表明在应用此变更集时必须删除 ./etc/my-app-config 这一资源,该条目的基础名称前会加上前缀 .wh. 。
7.6 Applying Changesets(应用变更集)
Layer Changesets of media type
application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tarare applied, rather than simply extracted as tar archives.媒体类型为 application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar 的层变更集被应用,而非简单地作为 tar 归档文件提取。
Applying a layer changeset requires special consideration for the whiteout files.
应用层变更集时,需要特别关注空白文件(whiteout files)。
In the absence of any whiteout files in a layer changeset, the archive is extracted like a regular tar archive.
若层变更集中不存在任何空白文件(whiteout files),则该归档文件会像常规 tar 归档文件一样被提取。
7.6.1 Changeset over existing files(现有文件的变更集)
This section specifies applying an entry from a layer changeset if the target path already exists.
本节规定了在目标路径已存在的情况下,如何从层变更集中应用条目。
If the entry and the existing path are both directories, then the existing path’s attributes MUST be replaced by those of the entry in the changeset. In all other cases, the implementation MUST do the semantic equivalent of the following:
若条目与现有路径均为目录,则现有路径的属性必须被变更集中条目的属性替换。所有其他的情况,实现方式必须在语义上等同于以下操作:
removing the file path (e.g.
unlink(2)on Linux systems)删除文件路径(例如,在 Linux 系统上使用 unlink (2) 函数)
recreating the file path, based on the contents and attributes of the changeset entry
根据变更集条目的内容和属性重新创建文件路径
7.7 Whiteouts(白障 )
A whiteout file is an empty file with a special filename that signifies a path should be deleted.
空白文件(whiteout file)是一种具有特殊文件名的空文件,用于标识某个路径应当被删除。
A whiteout filename consists of the prefix
.wh.plus the basename of the path to be deleted.空白文件的文件名由前缀
.wh.加上待删除路径的基础名称构成。As files prefixed with
.wh.are special whiteout markers, it is not possible to create a filesystem which has a file or directory with a name beginning with.wh..由于以
.wh.为前缀的文件是特殊的空白标记,因此无法创建包含名称以.wh.开头的文件或目录的文件系统。Once a whiteout is applied, the whiteout itself MUST also be hidden.
一旦空白文件(whiteout)被应用,该空白文件本身也必须被隐藏。
Whiteout files MUST only apply to resources in lower/parent layers.
*空白文件(whiteout files)仅能作用于更低层 / 父层中的资源。*
Files that are present in the same layer as a whiteout file can only be hidden by whiteout files in subsequent layers.
与空白文件(whiteout file)位于同一层中的文件,仅能被后续层中的空白文件隐藏。
The following is a base layer with several resources:
下面是一个基础层有的一些文件或者是目录资源:
1 | file1 |
If we then delete file1, file2, and b/, while leaving file3 and adding `file4, the next layer looks like:
如果我们随后删除 file1、file2 和 b/,同时保留 file3 并添加 file4,那么下一层将如下所示:
1 | .wh.file1 |
Note that regardless of the path being deleted, the whiteout file is a regular file in the archive.
注意!!!无论被删除的路径是什么,空白文件在归档中都是一个常规文件。
Implementations SHOULD generate layers such that the whiteout files appear before sibling directory entries.
实现方式应当生成层变更集,使空白文件出现在同级目录条目的前面。
7.7.1 Opaque Whiteout(不透明白障)
In addition to expressing that a single entry should be removed from a lower layer, layers may remove all of the children using an opaque whiteout entry.
除了表示应从更低层中移除单个条目外,层还可以通过不透明空白条目(opaque whiteout entry)移除某个目录下的所有子项。
An opaque whiteout entry is a file with the name
.wh..wh..opqindicating that all siblings are hidden in the lower layer.不透明空白条目(opaque whiteout entry)是一个文件名为
.wh..wh..opq的文件,用于标识更低层中该文件的所有同级项都应被隐藏。
Let’s take the following base layer as an example:
让我们使用下面的基础层做一个例子:
1 | etc/ |
If all children of bin/ are removed, the next layer would have the following:
如果把bin路径下的所有子目录全部删除,下一个层将会变成下面的样子:
1 | bin/ |
This is called opaque whiteout format. An opaque whiteout file hides all children of the bin/ including sub-directories and all descendants. Using explicit whiteout files, this would be equivalent to the following:
这被称为不透明空白文件格式(opaque whiteout format)。不透明空白文件会隐藏 bin/ 目录下的所有子项,包括子目录及其所有后代。如果使用显式空白文件,其效果等同于以下操作:
1 | bin/ |
In this case, a unique whiteout file is generated for each entry. If there were more children of bin/ in the base layer, there would be an entry for each. Note that this opaque file will apply to all children, including sub-directories, other resources and all descendants.
在这种情况下,会为每个条目生成一个唯一的空白文件。如果基础层中 bin/ 目录有更多子项,那么每个子项都会对应一个空白文件条目。请注意,此不透明空白文件将作用于所有子项,包括子目录、其他资源及其所有后代。
Implementations SHOULD generate layers using explicit whiteout files, but MUST accept both.
实现方式应当使用显式空白文件生成层变更集,但必须同时兼容这两种方式(显式空白文件和不透明空白文件)。
As another example, consider the following base layer:
再举一个例子,考虑以下基础层:
1 | a/ |
When the next layer is created, the original a/b directory is deleted and recreated with a/b/c/foo:
当创建下一层时,原始的 a/b 目录会被删除,然后重新创建并包含 a/b/c/foo:
1 | a/ |
When processing the second layer, a/.wh..wh..opq is applied first, before creating the new version of a/b, regardless of the ordering in which the whiteout file was encountered. For example, the following layer is equivalent to the layer above:
在处理第二层时,无论空白文件的实际出现顺序如何,都会先应用 a/.wh..wh..opq,再创建 a/b 的新版本。例如,以下层变更集与上面的层变更集是等效的:
1 | a/ |
Any given image is likely to be composed of several of these Image Filesystem Changeset tar archives.
任何给定的镜像都可能由若干个此类镜像文件系统变更集 tar 归档文件组成。
7.8 Non-Distributable Layers(不可分发层)
NOTE: Non-distributable layers are deprecated, and not recommended for future use. Implementations SHOULD NOT produce new non-distributable layers. Implementations are expected to support preexisting images with non-distributable layers.
注意:不可分发层已被弃用,不建议在未来使用。实现方式不应生成新的不可分发层,但应支持已存在的包含不可分发层的镜像。
Due to legal requirements, certain layers may not be regularly distributable. Such “non-distributable” layers are typically downloaded directly from a distributor but never uploaded.
由于法律要求,某些层可能无法常规分发。此类 “不可分发” 层通常直接从分发者处下载,但从不进行上传。
Non-distributable layers SHOULD be tagged with an alternative mediatype of application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar, application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip, or application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+zstd. Implementations SHOULD NOT upload layers tagged with this media type; however, such a media type SHOULD NOT affect whether an implementation downloads the layer.
不可分发层应当使用替代媒体类型进行标记,如 application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable.v1.tar+gzip,或 application/vnd.oci.image.layer.nondistributable。实现方式不应上传带有此媒体类型标记的层;但此媒体类型不应影响实现方式是否下载该层。
Descriptors referencing non-distributable layers MAY include urls for downloading these layers directly; however, the presence of the urls field SHOULD NOT be used to determine whether or not a layer is non-distributable.
引用不可分发层的描述符可包含直接下载这些层的 URL;但不应通过 urls 字段的存在来判断某一层是否为不可分发层。
8 OCI Image Configuration (OCI 镜像配置项)
An OCI Image is an ordered collection of root filesystem changes and the corresponding execution parameters for use within a container runtime. This specification outlines the JSON format describing images for use with a container runtime and execution tool and its relationship to filesystem changesets, described in Layers.
OCI镜像是一组有序的根文件系统变更集以及相应的提供容器运行时使用的运行参数。本小结概述了用于描述容器运行时和执行工具所使用的Json格式以及该格式与层中所描述的文件系统变更集的关系。
This section defines the application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json media type.
本小结定义使用的媒体类型是application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json
8.1 Terminology(术语)
This specification uses the following terms:
下面是本规范使用的属于列表:
8.1.1 Layer (层)
Image filesystems are composed of layers.
镜像文件系统由层(layers)组成。
Each layer represents a set of filesystem changes in a tar-based layer format, recording files to be added, changed, or deleted relative to its parent layer.
每个层都以基于 tar 的层格式表示一组文件系统变更,记录相对于其父层需要添加、修改或删除的文件。
Layers do not have configuration metadata such as environment variables or default arguments - these are properties of the image as a whole rather than any particular layer.
层不包含环境变量或默认参数等配置元数据 —— 这些是镜像整体的属性,而非任何一个层的属性。
Using a layer-based or union filesystem such as AUFS, or by computing the diff from filesystem snapshots, the filesystem changeset can be used to present a series of image layers as if they were one cohesive filesystem.
通过使用基于层的联合文件系统(如 AUFS),或者通过计算文件系统快照的差异,文件系统变更集可用于将一系列镜像层呈现为一个连贯的文件系统。
8.1.2 Image JSON (镜像Json)
Each image has an associated JSON structure which describes some basic information about the image such as date created, author, as well as execution/runtime configuration like its entrypoint, default arguments, networking, and volumes.
每个镜像都有一个关联的 JSON 结构,用于描述镜像的一些基本信息(如创建日期、作者),以及执行 / 运行时配置(如入口点、默认参数、网络设置和卷)。
The JSON structure also references a cryptographic hash of each layer used by the image, and provides history information for those layers.
该 JSON 结构还引用了镜像所使用的每个层的加密哈希值,并提供了这些层的历史信息。
This JSON is considered to be immutable, because changing it would change the computed ImageID.
此 JSON 结构被视为不可变的,因为对其进行修改会改变计算得出的镜像 ID(ImageID)。
Changing it means creating a new derived image, instead of changing the existing image.
对其进行修改意味着创建一个新的衍生镜像,而非更改现有镜像。
8.1.3 Layer DiffID (层DiffID)
A layer DiffID is the digest over the layer’s uncompressed tar archive and serialized in the descriptor digest format, e.g., sha256:a9561eb1b190625c9adb5a9513e72c4dedafc1cb2d4c5236c9a6957ec7dfd5a9. Layers SHOULD be packed and unpacked reproducibly to avoid changing the layer DiffID, for example by using tar-split to save the tar headers.
NOTE: Do not confuse DiffIDs with layer digests, often referenced in the manifest, which are digests over compressed or uncompressed content.
层的 DiffID 是对层的未压缩 tar 归档文件计算得出的摘要,并以描述符摘要格式进行序列化,例如:sha256:a9561eb1b190625c9adb5a9513e72c4dedafc1cb2d4c5236c9a6957ec7dfd5a9。层的打包和拆包过程应当具有可复现性,以避免改变层的 DiffID,例如可通过使用 tar-split 来保存 tar 头信息。
8.1.4 Layer ChainID (层链ID)
For convenience, it is sometimes useful to refer to a stack of layers with a single identifier. While a layer’s DiffID identifies a single changeset, the ChainID identifies the subsequent application of those changesets. This ensures that we have handles referring to both the layer itself, as well as the result of the application of a series of changesets. Use in combination with rootfs.diff_ids while applying layers to a root filesystem to uniquely and safely identify the result.
为方便起见,有时用单一标识符指代一叠层会很有用(译者注:stack表示一系列有顺序的层)。层的 DiffID 用于标识单个变更集,而 ChainID 则用于标识这些变更集的后续应用过程。这确保我们既能引用层本身,也能引用一系列变更集应用后的结果。在将层应用到根文件系统时,可结合 rootfs.diff_ids 使用 ChainID,以唯一且安全地标识应用结果。
8.1.4.1 Definition (定义)
The ChainID of an applied set of layers is defined with the following recursion:
已应用的一组层的 ChainID 通过以下递归方式定义:
1 | ChainID(L₀) = DiffID(L₀) |
For this, we define the binary | operation to be the result of applying the right operand to the left operand. For example, given base layer A and a changeset B, we refer to the result of applying B to A as A|B.
为此,我们将二元 | 运算符定义为将右操作数应用于左操作数所得到的结果。例如,给定基础层 A 和变更集 B,我们将把 B 应用于 A 所得到的结果称为 A|B。
Above, we define the ChainID for a single layer (L₀) as equivalent to the DiffID for that layer. Otherwise, the ChainID for a set of applied layers (L₀|...|Lₙ₋₁|Lₙ) is defined as the recursion Digest(ChainID(L₀|...|Lₙ₋₁) + " " + DiffID(Lₙ)).
上文已将单个层(L₁)的 ChainID 定义为与该层的 DiffID 相等。除此之外,一组已应用层(L₁|…|Lₙ₋₁|Lₙ)的 ChainID 按如下递归方式定义:Digest(ChainID(L₁|…|Lₙ₋₁) + “ “ + DiffID(Lₙ))。
8.1.4.2 Explanation (解释)
Let’s say we have layers A, B, C, ordered from bottom to top, where A is the base and C is the top. Defining | as a binary application operator, the root filesystem may be A|B|C. While it is implied that C is only useful when applied to A|B, the identifier C is insufficient to identify this result, as we’d have the equality C = A|B|C, which isn’t true.
假设我们有层 A、B、C,按从底到顶的顺序排列,其中 A 是基础层,C 是顶层。将 | 定义为二元应用运算符,那么根文件系统可以表示为 A|B|C。尽管显然只有将 C 应用于 A|B 时它才有用,但标识符 C 并不足以标识这一结果,因为这样会得出等式 (C = A|B|C),而这显然不成立。
The main issue is when we have two definitions of C, C = C and C = A|B|C. If this is true (with some handwaving), C = x|C where x = any application. This means that if an attacker can define x, relying on C provides no guarantee that the layers were applied in any order.
主要问题在于,当我们对 C 存在两种定义 ——(C = C) 和 (C = A|B|C) 时,如果这种情况成立(此处暂不深究细节),就会得出 (C = x|C),其中 x 可以是任何应用操作。这意味着,若攻击者能够定义x,那么依赖 C 根本无法保证各层是按特定顺序应用的。
The ChainID addresses this problem by being defined as a compound hash. We differentiate the changeset C, from the order-dependent application A|B|C by saying that the resulting rootfs is identified by ChainID(A|B|C), which can be calculated by ImageConfig.rootfs.
ChainID 通过被定义为复合哈希来解决这一问题。为区分变更集 C 与依赖顺序的应用结果 A|B|C,我们规定最终根文件系统由 ChainID (A|B|C) 标识,该值可通过 ImageConfig.rootfs 计算得出。
Let’s expand the definition of ChainID(A|B|C) to explore its internal structure:
让我们展开 ChainID (A|B|C) 的定义来探究其内部结构:
1 | ChainID(A) = DiffID(A) |
We can replace each definition and reduce to a single equality:
我们可以替换每一个定义,并简化为一个等式:
1 | ChainID(A|B|C) = Digest(Digest(DiffID(A) + " " + DiffID(B)) + " " + DiffID(C)) |
Hopefully, the above is illustrative of the actual contents of the ChainID. Most importantly, we can easily see that ChainID(C) != ChainID(A|B|C), otherwise, ChainID(C) = DiffID(C), which is the base case, could not be true.
希望以上内容能清晰说明 ChainID 的实际内涵。最重要的是,我们可以轻易看出 ChainID (C) ≠ ChainID (A|B|C);否则,作为基础情况的 ChainID (C) = DiffID (C) 就无法成立了。
8.1.5 ImageID (镜像ID)
Each image’s ID is given by the SHA256 hash of its configuration JSON. It is represented as a hexadecimal encoding of 256 bits, e.g., sha256:a9561eb1b190625c9adb5a9513e72c4dedafc1cb2d4c5236c9a6957ec7dfd5a9. Since the configuration JSON that gets hashed references hashes of each layer in the image, this formulation of the ImageID makes images content-addressable.
每个镜像的 ID 由其配置 JSON 的 SHA256 哈希值决定,以 256 位的十六进制编码形式表示,例如:sha256:a9561eb1b190625c9adb5a9513e72c4dedafc1cb2d4c5236c9a6957ec7dfd5a9。由于被哈希计算的配置 JSON 引用了镜像中每个层的哈希值,因此这种镜像 ID 的生成方式使镜像具备了内容可寻址性。
8.2 Properties(属性)
Note: Any OPTIONAL field MAY also be set to null, which is equivalent to being absent.
注意:任何可选字段也可以设置为 null,这等同于该字段不存在。
created string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
An combined date and time at which the image was created, formatted as defined by RFC 3339, section 5.6.
镜像的创建日期和时间组合,格式遵循 RFC 3339 标准第 5.6 节的规定(url: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3339#section-5.6)。
author string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
Gives the name and/or email address of the person or entity which created and is responsible for maintaining the image.
提供创建该镜像并负责维护它的个人或实体的名称和 / 或电子邮件地址。
architecture string, REQUIRED 字符型,必填
The CPU architecture which the binaries in this image are built to run on. Configurations SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand, values listed in the Go Language document for
GOARCH.此镜像中的二进制文件所适配运行的 CPU 架构。配置应当使用且实现应当理解 Go 语言文档中为
GOARCH列出的值。os string, REQUIRED 字符型,可选填
The name of the operating system which the image is built to run on. Configurations SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand, values listed in the Go Language document for
GOOS.该内容描述的是镜像所适配运行的操作系统名称。配置应当使用且实现应当理解 Go 语言文档中为
GOOS列出的值,以此确保镜像在对应的操作系统环境中能够正确运行。os.version string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
This OPTIONAL property specifies the version of the operating system targeted by the referenced blob. Implementations MAY refuse to use manifests where
os.versionis not known to work with the host OS version. Valid values are implementation-defined. e.g.10.0.14393.1066onwindows.此可选属性指定引用的二进制大对象(blob)所针对的操作系统版本。实现程序可以拒绝使用那些
os.version与主机操作系统版本不兼容的清单。有效值由实现方式定义,例如在 Windows 系统上可为 10.0.14393.1066。os.features array of strings, OPTIONAL 字符数组,可选填
This OPTIONAL property specifies an array of strings, each specifying a mandatory OS feature. When
osiswindows, image indexes SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand the following values:此可选属性指定一个字符串数组,其中每个字符串都表示一项必需的操作系统功能。当操作系统为 Windows 时,镜像索引应当使用且实现程序应当理解以下值:
win32k: image requireswin32k.syson the host (Note:win32k.sysis missing on Nano Server)win32k:镜像要求主机上存在 win32k.sys(注:Nano Server 上不存在 win32k.sys)
variant string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
The variant of the specified CPU architecture. Configurations SHOULD use, and implementations SHOULD understand,
variantvalues listed in the Platform Variants table.指定 CPU 架构的变体。配置应当使用且实现程序应当理解《平台变体表》中列出的变体值。
config object, OPTIONAL 对象型,可选填
The execution parameters which SHOULD be used as a base when running a container using the image. This field can be
null, in which case any execution parameters should be specified at creation of the container.运行使用该镜像的容器时应作为基础的执行参数。此字段可以为 null,在这种情况下,任何执行参数都应在容器创建时指定。
User string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
The username or UID which is a platform-specific structure that allows specific control over which user the process run as. This acts as a default value to use when the value is not specified when creating a container. For Linux based systems, all of the following are valid:
user,uid,user:group,uid:gid,uid:group,user:gid. Ifgroup/gidis not specified, the default group and supplementary groups of the givenuser/uidin/etc/passwdand/etc/groupfrom the container are applied. Ifgroup/gidis specified, supplementary groups from the container are ignored.用户名或 UID 是一种特定于平台的结构,它允许对进程运行时所使用的用户进行精确控制。这一值会作为默认值使用,当创建容器时未指定用户相关值时,便会采用此默认值。对于基于 Linux 的系统,以下所有形式都是有效的:用户名、UID、用户名:组名、UID:GID、UID: 组名、用户名:GID。如果未指定组 / GID,将会应用容器中 /etc/passwd 和 /etc/group 文件里给定用户 / UID 对应的默认组以及附加组。如果指定了组 / GID,则会忽略容器中的附加组。
ExposedPorts object, OPTIONAL 对象型,可选填
A set of ports to expose from a container running this image. Its keys can be in the format of:
port/tcp,port/udp,portwith the default protocol beingtcpif not specified. These values act as defaults and are merged with any specified when creating a container. NOTE: This JSON structure value is unusual because it is a direct JSON serialization of the Go typemap[string]struct{}and is represented in JSON as an object mapping its keys to an empty object.一组需要从运行此镜像的容器中暴露的端口。其键的格式可以是:port/tcp、port/udp,若未指定协议,端口的默认协议为 tcp。这些值作为默认值,会与创建容器时指定的任何端口设置合并。注意:此 JSON 结构的值较为特殊,因为它是 Go 类型
map[string]struct{}的直接 JSON 序列化结果,在 JSON 中表现为一个将键映射到空对象的对象。Env array of strings, OPTIONAL
Entries are in the format of
VARNAME=VARVALUE. These values act as defaults and are merged with any specified when creating a container.条目格式为 VARNAME=VARVALUE。这些值作为默认值,会与创建容器时指定的任何值合并。
Entrypoint array of strings, OPTIONAL 字符型数组,可选填
A list of arguments to use as the command to execute when the container starts. These values act as defaults and may be replaced by an entrypoint specified when creating a container.
容器启动时用作执行命令的参数列表。这些值作为默认参数,可能会被创建容器时指定的入口点替换。
Cmd array of strings, OPTIONAL 字符型数组,可选填
Default arguments to the entrypoint of the container. These values act as defaults and may be replaced by any specified when creating a container. If an
Entrypointvalue is not specified, then the first entry of theCmdarray SHOULD be interpreted as the executable to run.容器入口点的默认参数。这些值作为默认值,可能会被创建容器时指定的任何参数替换。如果未指定 Entrypoint 值,则 Cmd 数组的第一个条目应当被解释为要运行的可执行文件。
Volumes object, OPTIONAL 对象型,可选填
A set of directories describing where the process is likely to write data specific to a container instance. NOTE: This JSON structure value is unusual because it is a direct JSON serialization of the Go type
map[string]struct{}and is represented in JSON as an object mapping its keys to an empty object.一组目录,用于描述进程可能写入容器实例特定数据的位置。注意:此 JSON 结构的值较为特殊,因为它是 Go 类型
map[string]struct{}的直接 JSON 序列化结果,在 JSON 中表现为一个将键映射到空对象的对象。WorkingDir string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
Sets the current working directory of the entrypoint process in the container. This value acts as a default and may be replaced by a working directory specified when creating a container.
设置容器中入口点进程的当前工作目录。此值作为默认值,可能会被创建容器时指定的工作目录替换。
Labels object, OPTIONAL 对象型,可选填
This field contains arbitrary metadata for the container. This property MUST use the annotation rules.
此字段包含容器的任意元数据。此属性必须遵循注解规则。
StopSignal string, OPTIONAL
This field contains the system call signal that will be sent to the container to exit. The signal can be a signal name in the format
SIGNAME, for instanceSIGKILLorSIGRTMIN+3.此字段包含将发送给容器以使其退出的系统调用信号。该信号可以是 SIGNAME 格式的信号名称,例如 SIGKILL 或 SIGRTMIN+3。
ArgsEscaped boolean, OPTIONAL 布尔型,可选填
[Deprecated]- This field is present only for legacy compatibility with Docker and should not be used by new image builders. It is used by Docker for Windows images to indicate that theEntrypointorCmdor both, contains only a single element array, that is a pre-escaped, and combined into a single stringCommandLine. Iftruethe value inEntrypointorCmdshould be used as-is to avoid double escaping. Note, the exact behavior ofArgsEscapedis complex and subject to implementation details in Moby project.[已弃用] - 此字段仅为与 Docker 的遗留兼容性而存在,新的镜像构建工具不应使用。Docker 在 Windows 镜像中使用此字段,用于表明 Entrypoint、Cmd 或两者均包含一个单元素数组,该数组是经过预转义并合并为单个字符串命令行(CommandLine)的。如果该字段为 true,则 Entrypoint 或 Cmd 中的值应按原样使用,以避免双重转义。请注意,ArgsEscaped 的具体行为较为复杂,且取决于 Moby 项目的实现细节。
Memory integer, OPTIONAL 整型,可选填
This property is reserved for use, to maintain compatibility.
保留字段,为了以后可能使用。
MemorySwap integer, OPTIONAL
This property is reserved for use, to maintain compatibility.
保留字段,为了以后可能使用。
CpuShares integer, OPTIONAL
This property is reserved for use, to maintain compatibility.
保留字段,为了以后可能使用。
Healthcheck object, OPTIONAL
This property is reserved for use, to maintain compatibility.
保留字段,为了以后可能使用。
rootfs object, REQUIRED 对象型,必填
The rootfs key references the layer content addresses used by the image. This makes the image config hash depend on the filesystem hash.
rootfs键引用镜像所使用的层内容地址。这使得镜像配置哈希值依赖于文件系统哈希值。type string, REQUIRED 字符型,必填
MUST be set to
layers. Implementations MUST generate an error if they encounter a unknown value while verifying or unpacking an image.*必须设置为
layers。实现程序在验证或解包镜像时若遇到未知值,必须生成错误。*diff_ids array of strings, REQUIRED 字符型数组,必填
An array of layer content hashes (
DiffIDs), in order from first to last.层内容哈希值(DiffID)的数组,按从第一个到最后一个的顺序排列。
history array of objects, OPTIONAL 对象数组,选填
Describes the history of each layer. The array is ordered from first to last. The object has the following fields:
描述每一层的历史记录。该数组按从第一个到最后一个的顺序排列。此对象包含以下字段:
created string, OPTIONAL 字符型,选填
A combined date and time at which the layer was created, formatted as defined by RFC 3339, section 5.6.
层创建的日期和时间组合,格式遵循 RFC 3339 第 5.6 节的规定(url: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3339#section-5.6)。
author string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
The author of the build point.
构建节点的作者。
created_by string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
The command which created the layer.
创建该层的命令。
comment string, OPTIONAL 字符型,可选填
A custom message set when creating the layer.
创建该层时设置的自定义消息。
empty_layer boolean, OPTIONAL 布尔型,可选填
This field is used to mark if the history item created a filesystem diff. It is set to true if this history item doesn’t correspond to an actual layer in the rootfs section (for example, Dockerfile’s ENV command results in no change to the filesystem).
此字段用于标记历史记录项是否创建了文件系统差异。如果该历史记录项与
rootfs部分中的实际层不对应(例如,Dockerfile 的ENV命令未对文件系统产生任何更改),则该字段会被设置为true。
Any extra fields in the Image JSON struct are considered implementation specific and MUST NOT generate an error by any implementations which are unable to interpret them.
*镜像 JSON 结构中的任何额外字段均被视为特定于实现的内容,对于无法解释这些字段的任何实现程序,不得因此生成错误。*
Whitespace is OPTIONAL and implementations MAY have compact JSON with no whitespace.
空白字符为可选项,实现程序可以采用无空白字符的紧凑 JSON 格式。
8.2.1 Example (示例)
Here is an example image configuration JSON document:
下面是一份镜像配置文件的示例:
1 | { |
9 Annotations (注解)
Several components of the specification, like Image Manifests and Descriptors, feature an optional annotations property, whose format is common and defined in this section.
本规范的多个组件(如镜像清单和描述符)包含一个可选的 annotations 属性,其格式具有通用性,并在本节中定义。
This property contains arbitrary metadata.
此属性包含任意元数据。
9.1 Rules(规则)
Annotations MUST be a key-value map where both the key and value MUST be strings.
*注解(Annotations)必须是一个键值映射,其中键和值都必须是字符串类型。*
While the value MUST be present, it MAY be an empty string.
尽管值必须存在,但它可以是一个空字符串。
Keys MUST be unique within this map, and best practice is to namespace the keys.
键在该映射中必须是唯一的,并且最佳实践是对键进行命名空间划分。
Keys SHOULD be named using a reverse domain notation - e.g.
com.example.myKey.键应当使用反向域名表示法命名,例如
com.example.myKey。The prefix
org.opencontainersis reserved for keys defined in Open Container Initiative (OCI) specifications and MUST NOT be used by other specifications and extensions.前缀
org.opencontainers专为开放容器倡议(OCI)规范中定义的键保留,其他规范和扩展不得使用该前缀。Keys using the
org.opencontainers.imagenamespace are reserved for use in the OCI Image Specification and MUST NOT be used by other specifications and extensions, including other OCI specifications.*使用
org.opencontainers.image命名空间的键专为开放容器倡议(OCI)镜像规范保留使用,其他规范和扩展(包括其他 OCI 规范)不得使用这些键。*If there are no annotations then this property MUST either be absent or be an empty map.
若不存在注解(annotations),则此属性必须要么缺失,要么为一个空映射。
Consumers MUST NOT generate an error if they encounter an unknown annotation key.
*消费者在遇到未知的注解键时,不得生成错误。*
9.2 Pre-Defined Annotation Keys (预定义注解键)
This specification defines the following annotation keys, intended for but not limited to image index, image manifest, and descriptor authors.
本规范定义了以下注解键,其适用对象包括但不限于镜像索引、镜像清单和描述符的作者。
org.opencontainers.image.created date and time on which the image was built, conforming to RFC 3339.
org.opencontainers.image.created:镜像的构建日期和时间,需符合 RFC 3339 标准(字符串类型)(url: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3339#section-5.6)。org.opencontainers.image.authors contact details of the people or organization responsible for the image (freeform string)
org.opencontainers.image.authors:负责该镜像的人员或组织的联系信息(自由格式字符串)。org.opencontainers.image.url URL to find more information on the image (string)
org.opencontainers.image.url:用于查找该镜像更多信息的 URL(字符串类型)org.opencontainers.image.documentation URL to get documentation on the image (string)
org.opencontainers.image.documentation:用于获取该镜像文档的 URL(字符串类型)。org.opencontainers.image.source URL to get source code for building the image (string)
org.opencontainers.image.source:用于获取构建该镜像的源代码的 URL(字符串类型)。org.opencontainers.image.version version of the packaged software
org.opencontainers.image.version:打包软件的版本(字符串类型)The version MAY match a label or tag in the source code repository
该版本可以与源代码仓库中的标签(label)或标记(tag)相匹配。
version MAY be Semantic versioning-compatible
该版本可以与语义化版本控制(Semantic Versioning)兼容。
org.opencontainers.image.revision Source control revision identifier for the packaged software.
*org.opencontainers.image.revision:打包软件的源代码控制修订标识符(字符串类型)。*org.opencontainers.image.vendor Name of the distributing entity, organization or individual.
org.opencontainers.image.vendor:分发实体、组织或个人的名称(字符串类型)。org.opencontainers.image.licenses License(s) under which contained software is distributed as an SPDX License Expression.
org.opencontainers.image.licenses:包含的软件所依据的许可证,以 SPDX 许可证表达式形式呈现。org.opencontainers.image.ref.name Name of the reference for a target (string).
org.opencontainers.image.ref.name:目标引用的名称(字符串类型)。SHOULD only be considered valid when on descriptors on
index.jsonwithin image layout.仅在镜像布局中
index.json的描述符上时,才应被视为有效。Character set of the value SHOULD conform to alphanum of
A-Za-z0-9and separator set of-._:@/+该值的字符集应符合 A-Za-z0-9 等字母数字字符,以及 -._:@/+ 等分隔符集。
A valid reference matches the following grammar:
有效的引用需符合以下语法规则:
1
2
3
4ref ::= component ("/" component)*
component ::= alphanum (separator alphanum)*
alphanum ::= [A-Za-z0-9]+
separator ::= [-._:@+] | "--"
org.opencontainers.image.title Human-readable title of the image (string)
org.opencontainers.image.title:镜像的人类可读标题(字符串类型)org.opencontainers.image.description Human-readable description of the software packaged in the image (string)
org.opencontainers.image.description:镜像中打包的软件的人类可读描述(字符串类型)org.opencontainers.image.base.digest Digest of the image this image is based on (string)
org.opencontainers.image.base.digest:当前镜像所基于的基础镜像的摘要(字符串类型)This SHOULD be the immediate image sharing zero-indexed layers with the image, such as from a Dockerfile
FROMstatement.这应当是与当前镜像共享零索引层的直接基础镜像,例如来自 Dockerfile 中的 FROM 语句所指定的镜像。
This SHOULD NOT reference any other images used to generate the contents of the image (e.g., multi-stage Dockerfile builds).
这不应引用任何用于生成镜像内容的其他镜像(例如,多阶段 Dockerfile 构建中的镜像)。
org.opencontainers.image.base.name Image reference of the image this image is based on (string)
org.opencontainers.image.base.name:当前镜像所基于的基础镜像的引用(字符串类型)This SHOULD be image references in the format defined by distribution/distribution.
符合 distribution/distribution 所定义格式的镜像引用。
This SHOULD be a fully qualified reference name, without any assumed default registry. (e.g.,
registry.example.com/my-org/my-image:taginstead ofmy-org/my-image:tag).这应当是一个完全限定的引用名称,不包含任何默认注册表的假设(例如,应使用
registry.example.com/my-org/my-image:tag,而非my-org/my-image:tag)。This SHOULD be the immediate image sharing zero-indexed layers with the image, such as from a Dockerfile
FROMstatement.这应当是与当前镜像共享零索引层的直接基础镜像,例如来自 Dockerfile 中 FROM 语句所指定的镜像。
This SHOULD NOT reference any other images used to generate the contents of the image (e.g., multi-stage Dockerfile builds).
这不应引用任何用于生成镜像内容的其他镜像(例如,多阶段 Dockerfile 构建中的镜像)。
If the
image.base.nameannotation is specified, theimage.base.digestannotation SHOULD be the digest of the manifest referenced by theimage.ref.nameannotation.如果指定了
image.base.name注解,则image.base.digest注解应当是image.ref.name注解所引用的清单的摘要。
9.3 Back-compatibility with Label Schema (向后兼容性的标签设计)
Label Schema defined a number of conventional labels for container images, and these are now superseded by annotations with keys starting org.opencontainers.image.
标签架构(Label Schema)为容器镜像定义了一系列常规标签,而这些标签如今已被键以 org.opencontainers.image 开头的注解所取代。
While users are encouraged to use the org.opencontainers.image keys, tools MAY choose to support compatible annotations using the org.label-schema prefix as follows.
虽然鼓励用户使用 org.opencontainers.image 系列键,但工具可以选择按如下方式支持使用 org.label-schema 前缀的兼容注解。
org.opencontainers.image prefix |
org.label-schema prefix |
Compatibility notes |
|---|---|---|
created |
build-date |
Compatible |
url |
url |
Compatible |
source |
vcs-url |
Compatible |
version |
version |
Compatible |
revision |
vcs-ref |
Compatible |
vendor |
vendor |
Compatible |
title |
name |
Compatible |
description |
description |
Compatible |
documentation |
usage |
Value is compatible if the documentation is located by a URL |
authors |
No equivalent in Label Schema | |
licenses |
No equivalent in Label Schema | |
ref.name |
No equivalent in Label Schema | |
schema-version |
No equivalent in the OCI Image Spec | |
docker.*, rkt.* |
No equivalent in the OCI Image Spec |
10 Conversion to OCI Runtime Configuration (转换为OCI运行时配置)
When extracting an OCI Image into an OCI Runtime bundle, two orthogonal components of the extraction are relevant:
将 OCI 镜像提取到 OCI 运行时捆绑包时,提取过程中有两个相互独立的组件与之相关:
Extraction of the root filesystem from the set of filesystem layers.
从文件系统层集合中提取根文件系统。
Conversion of the image configuration blob to an OCI Runtime configuration blob.
将镜像配置 blob 转换为 OCI 运行时配置 blob。
This section defines how to convert an application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json blob to an OCI runtime configuration blob (the latter component of extraction). The former component of extraction is defined elsewhere and is orthogonal to configuration of a runtime bundle. The values of runtime configuration properties not specified by this document are implementation-defined.
本节定义了如何将 application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json 格式的 blob 转换为 OCI 运行时配置 blob(即提取过程的后一个组件)。提取过程的前一个组件在其他地方定义,且与运行时捆绑包的配置相互独立。本文档未指定的运行时配置属性值由具体实现定义。
A converter MUST rely on the OCI image configuration to build the OCI runtime configuration as described by this document; this will create the “default generated runtime configuration”.
转换器必须依据本文档所述,依赖 OCI 镜像配置来构建 OCI 运行时配置;这将生成 “默认生成的运行时配置”。
The “default generated runtime configuration” MAY be overridden or combined with externally provided inputs from the caller. In addition, a converter MAY have its own implementation-defined defaults and extensions which MAY be combined with the “default generated runtime configuration”. The restrictions in this document refer only to combining implementation-defined defaults with the “default generated runtime configuration”. Externally provided inputs are considered to be a modification of the application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json used as a source, and such modifications have no restrictions.
“默认生成的运行时配置” 可以被调用方提供的外部输入覆盖或组合。此外,转换器可以有其自身的实现定义的默认值和扩展,这些默认值和扩展可以与 “默认生成的运行时配置” 相结合。本文档中的限制仅涉及将实现定义的默认值与 “默认生成的运行时配置” 进行组合的情况。外部提供的输入被视为对用作源的 application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json 的修改,此类修改不受任何限制。
For example, externally provided inputs MAY cause an environment variable to be added, removed or changed. However an implementation-defined default SHOULD NOT result in an environment variable being removed or changed.
例如,外部提供的输入可以对环境变量进行添加、删除或修改操作。但是,由实现定义的默认值不应导致环境变量被删除或修改。
10.1 Verbatim Fields(字段对照)
Certain image configuration fields have an identical counterpart in the runtime configuration. Some of these are purely annotation-based fields, and have been extracted into a separate subsection. A compliant configuration converter MUST extract the following fields verbatim to the corresponding field in the generated runtime configuration:
某些镜像配置字段在运行时配置中存在完全对应的字段。其中一些是纯粹基于注解的字段,已被提取到单独的小节中。符合规范的配置转换器必须将以下字段原样提取到生成的运行时配置的对应字段中:
| Image Field | Runtime Field | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Config.WorkingDir |
process.cwd |
|
Config.Env |
process.env |
1 |
Config.Entrypoint |
process.args |
2 |
Config.Cmd |
process.args |
2 |
The converter MAY add additional entries to
process.envbut it SHOULD NOT add entries that have variable names present inConfig.Env.转换器可以向
process.env中添加额外的条目,但不应添加那些在Config.Env中已存在变量名的条目。If both
Config.EntrypointandConfig.Cmdare specified, the converter MUST append the value ofConfig.Cmdto the value ofConfig.Entrypointand setprocess.argsto that combined value.若同时指定了
Config.Entrypoint和Config.Cmd,转换器必须将Config.Cmd的值追加到Config.Entrypoint的值之后,并将process.args设置为该组合后的值。
10.2 Annotation Fields (注解字段)
These fields all affect the annotations of the runtime configuration, and are thus subject to precedence.
这些字段均会影响运行时配置的注解,因此需遵循优先级规则。
| Image Field | Runtime Field | Notes |
|---|---|---|
os |
annotations |
1,2 |
architecture |
annotations |
1,3 |
variant |
annotations |
1,4 |
os.version |
annotations |
1,5 |
os.features |
annotations |
1,6 |
author |
annotations |
1,7 |
created |
annotations |
1,8 |
Config.Labels |
annotations |
|
Config.StopSignal |
annotations |
1,9 |
If a user has explicitly specified this annotation with
Config.Labels, then the value specified in this field takes lower precedence and the converter MUST instead use the value fromConfig.Labels.若用户已通过
Config.Labels明确指定此注解,则该字段中指定的值优先级较低,转换器必须改用Config.Labels中的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.osinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.os的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.architectureinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.architecture的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.variantinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.variant的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.os.versioninannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.os.version的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.os.featuresinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.os.features的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.authorinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.author的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.createdinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.created的值。The value of this field MUST be set as the value of
org.opencontainers.image.stopSignalinannotations.该字段的值必须被设置为注解中
org.opencontainers.image.stopSignal的值。
10.3 Parsed Fields (解析的字段)
Certain image configuration fields have a counterpart that must first be translated. A compliant configuration converter SHOULD parse all of these fields and set the corresponding fields in the generated runtime configuration:
某些镜像配置字段存在对应的字段,但这些对应字段必须先经过转换。符合规范的配置转换器应当解析所有这些字段,并在生成的运行时配置中设置对应的字段:
| Image Field | Runtime Field |
|---|---|
Config.User |
process.user.* |
The method of parsing the above image fields are described in the following sections.
解析上述镜像字段的方法将在以下章节中阐述。
Config.User
If the values of user or group in Config.User are numeric (uid or gid) then the values MUST be copied verbatim to process.user.uid and process.user.gid respectively. If the values of user or group in Config.User are not numeric (user or group) then a converter SHOULD resolve the user information using a method appropriate for the container’s context. For Unix-like systems, this MAY involve resolution through NSS or parsing /etc/passwd from the extracted container’s root filesystem to determine the values of process.user.uid and process.user.gid.
若 Config.User 中的用户(user)或组(group)值为数字形式(即用户 ID 或组 ID),则这些值必须分别原样复制到 process.user.uid 和 process.user.gid 中。若 Config.User 中的用户或组值非数字形式(即用户名或组名),则转换器应当使用适合容器上下文的方法解析用户信息。对于类 Unix 系统,这可能包括通过 NSS(名称服务交换)进行解析,或从提取的容器根文件系统中解析 /etc/passwd 文件,以确定 process.user.uid 和 process.user.gid 的值。
In addition, a converter SHOULD set the value of process.user.additionalGids to a value corresponding to the user in the container’s context described by Config.User. For Unix-like systems, this MAY involve resolution through NSS or parsing /etc/group and determining the group memberships of the user specified in process.user.uid. The converter SHOULD NOT modify process.user.additionalGids if the value of user in Config.User is numeric or if Config.User specifies a group.
此外,转换器应当将 process.user.additionalGids 的值设置为与 Config.User 所描述的容器上下文中的用户相对应的值。对于类 Unix 系统,这可能包括通过 NSS(名称服务交换)进行解析,或解析 /etc/group 文件并确定 process.user.uid 中指定用户的组成员身份。若 Config.User 中的用户值为数字形式,或 Config.User 已指定了组,则转换器不应修改 process.user.additionalGids 的值。
If Config.User is not defined, the converted process.user value is implementation-defined. If Config.User does not correspond to a user in the container’s context, the converter MUST return an error.
若未定义 Config.User,则转换后的 process.user 值由实现定义。若 Config.User 与容器上下文中的用户不匹配,转换器必须返回错误。
10.4 Optional Fields (可选的字段)
Certain image configuration fields are not applicable to all conversion use cases, and thus are optional for configuration converters to implement. A compliant configuration converter SHOULD provide a way for users to extract these fields into the generated runtime configuration:
某些镜像配置字段并非适用于所有转换场景,因此配置转换器对这些字段的实现是可选的。符合规范的配置转换器应当为用户提供一种将这些字段提取到生成的运行时配置中的方式:
| Image Field | Runtime Field | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Config.ExposedPorts |
annotations |
1 |
Config.Volumes |
mounts |
2 |
The runtime configuration does not have a corresponding field for this image field. However, converters SHOULD set the
org.opencontainers.image.exposedPortsannotation.运行时配置中没有与该镜像字段对应的字段。不过,转换器应当设置
org.opencontainers.image.exposedPorts注解。Implementations SHOULD provide mounts for these locations such that application data is not written to the container’s root filesystem. If a converter implements conversion for this field using mountpoints, it SHOULD set the
destinationof the mountpoint to the value specified inConfig.Volumes. An implementation MAY seed the contents of the mount with data in the image at the same location. If a new image is created from a container based on the image described by this configuration, data in these paths SHOULD NOT be included in the new image. The othermountsfields are platform and context dependent, and thus are implementation-defined. Note that the implementation ofConfig.Volumesneed not use mountpoints, as it is effectively a mask of the filesystem.实现应当为这些位置提供挂载,以确保应用数据不会写入容器的根文件系统。若转换器通过挂载点对该字段进行转换实现,则应当将挂载点的目标路径设置为
Config.Volumes中指定的值。实现可以使用镜像中相同位置的数据来初始化挂载内容。若基于此配置所描述的镜像从容器创建新镜像,则这些路径中的数据不应包含在新镜像中。其他挂载字段取决于平台和上下文,因此由实现定义。请注意,Config.Volumes的实现无需使用挂载点,因为它本质上是文件系统的一种掩码。
Config.ExposedPorts
The OCI runtime configuration does not provide a way of expressing the concept of “container exposed ports”. However, converters SHOULD set the org.opencontainers.image.exposedPorts annotation, unless doing so will cause a conflict.
OCI 运行时配置没有提供表达 “容器暴露端口” 这一概念的方式。不过,转换器应当设置 org.opencontainers.image.exposedPorts 注解,除非这样做会导致冲突。
org.opencontainers.image.exposedPorts is the list of values that correspond to the keys defined for Config.ExposedPorts (string, comma-separated values).
org.opencontainers.image.exposedPorts 是与 Config.ExposedPorts 中定义的键相对应的值列表(字符串形式,以逗号分隔)。
10.5 Annotations (注解)
There are three ways of annotating an OCI image in this specification:
本规范中定义了三种为 OCI 镜像添加注解的方式:
Config.Labelsin the configuration of the image.镜像配置中的
Config.Labels。annotationsin the manifest of the image.镜像清单中的
annotations(注解)。annotationsin the image index of the image.镜像索引中的
annotations(注解)。
In addition, there are also implicit annotations that are defined by this section which are determined from the values of the image configuration. A converter SHOULD NOT attempt to extract annotations from manifests or image indices. If there is a conflict (same key but different value) between an implicit annotation (or annotation in manifests or image indices) and an explicitly specified annotation in Config.Labels, the value specified in Config.Labels MUST take precedence.
此外,本节还定义了一些隐式注解,这些注解由镜像配置的值确定。转换器不应尝试从清单或镜像索引中提取注解。若隐式注解(或清单、镜像索引中的注解)与 Config.Labels 中显式指定的注解存在冲突(键相同但值不同),则 Config.Labels 中指定的值必须优先生效。
A converter MAY add annotations which have keys not specified in the image. A converter MUST NOT modify the values of annotations specified in the image.
转换器可以添加键未在镜像中指定的注解。但转换器不得修改镜像中已指定的注解的值。
11 Considerations(注意事项)
11.1 Extensibility(可扩展性)
Implementations storing or copying content MUST NOT modify or alter the content in a way that would change the digest of the content. Examples of these implementations include:
存储或复制内容的实现不得以会改变内容摘要的方式修改或更改内容。此类实现的示例包括:
A registry implementing the distribution specification, including local registries, caching proxies
实现分发规范的注册表,包括本地注册表、缓存代理。
An application which copies content to disk or between registries
将内容复制到磁盘或在注册表之间复制内容的应用程序。
Implementations processing content SHOULD NOT generate an error if they encounter an unknown property in a known media type. Examples of these implementations include:
*处理内容的实现若在已知媒体类型中遇到未知属性,不应生成错误。此类实现的示例包括:*
A runtime implementing the runtime specification
实现运行时规范的运行时(环境)(url: https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec)
An implementation using OCI to retrieve and utilize artifacts, e.g.: a WASM runtime
使用 OCI 检索和利用制品的实现,例如:WebAssembly 运行时。
11.2 Canonicalization(规范化)
OCI Images are content-addressable. See descriptors for more.
OCI 镜像采用内容寻址方式。更多信息参见描述符。
One benefit of content-addressable storage is easy deduplication.
内容寻址存储的一个优势是便于实现重复数据删除。
Many images might depend on a particular layer, but there will only be one blob in the store.
许多镜像可能依赖于某个特定的层,但存储中只会存在一个对应的二进制大对象(blob)。
With a different serialization, that same semantic layer would have a different hash, and if both versions of the layer are referenced there will be two blobs with the same semantic content.
若采用不同的序列化方式,相同语义的层会产生不同的哈希值;如果这两个版本的层都被引用,存储中就会出现两个语义内容相同但哈希不同的二进制大对象(blob)。
To allow efficient storage, implementations serializing content for blobs SHOULD use a canonical serialization.
为实现高效存储,对二进制大对象(blob)内容进行序列化的实现应当采用规范化的序列化方式。
This increases the chance that different implementations can push the same semantic content to the store without creating redundant blobs.
这会提高不同实现将相同语义内容推送到存储中时不会产生冗余二进制大对象(blob)的可能性。
11.2.1 JSON
JSON content SHOULD be serialized as canonical JSON. Of the OCI Image Format Specification media types, all the types ending in +json contain JSON content. Implementations:
JSON 内容应当以规范化 JSON 格式进行序列化。在 OCI 镜像格式规范的媒体类型中,所有以 +json 结尾的类型均包含 JSON 内容。各实现需注意:
Go: github.com/docker/go, which claims to implement canonical JSON except for Unicode normalization.
Go 语言:github.com/docker/go,该库声称实现了规范化 JSON,但不包含 Unicode 归一化功能。
11.3 EBNF(扩展巴科斯 - 瑙尔范式)
For field formats described in this specification, we use a limited subset of Extended Backus-Naur Form, similar to that used by the XML specification. Grammars present in the OCI specification are regular and can be converted to a single regular expressions. However, regular expressions are avoided to limit ambiguity between regular expression syntax. By defining a subset of EBNF used here, the possibility of variation, misunderstanding or ambiguities from linking to a larger specification can be avoided.
对于本规范中描述的字段格式,我们采用了扩展巴科斯 - 瑙尔范式(Extended Backus-Naur Form)的一个有限子集,其风格与 XML 规范所使用的范式相似。OCI 规范中给出的语法均为正则语法,且可转换为单一的正则表达式。然而,为减少正则表达式语法之间的歧义,我们避免直接使用正则表达式。通过在此处定义所使用的 EBNF 子集,能够避免因引用更庞大的规范而可能产生的差异、误解或歧义问题。
Grammars are made up of rules in the following form:
语法由以下形式的规则构成:
1 | symbol ::= expression |
We can say we have the production identified by symbol if the input is matched by the expression. Whitespace is completely ignored in rule definitions.
如果输入与表达式匹配,我们就可以说存在由该符号标识的产生式。在规则定义中,空白字符会被完全忽略。
11.3.1 Expressions
The simplest expression is the literal, surrounded by quotes:
最简单的表达式是被引号包围的字面量:
1 | literal ::= "matchthis" |
The above expression defines a symbol, “literal”, that matches the exact input of “matchthis”. Character classes are delineated by brackets ([]), describing either a set, range or multiple range of characters:
上述表达式定义了一个符号 “literal”,它匹配 “matchthis” 这一精确输入。字符类由方括号([])界定,用于描述字符的集合、范围或多个范围:
1 | set := [abc] |
The above symbol “set” would match one character of either “a”, “b” or “c”. The symbol “range” would match any character, “A” to “Z”, inclusive. Currently, only matching for 7-bit ascii literals and character classes is defined, as that is all that is required by this specification. Multiple character ranges and explicit characters can be specified in a single character classes, as follows:
上述符号 “set” 将匹配 “a”“b” 或 “c” 中的任意一个字符。符号 “range” 将匹配从 “A” 到 “Z”(含 “A” 和 “Z”)的任意字符。目前,仅定义了 7 位 ASCII 字面量和字符类的匹配规则,因为这是本规范所需的全部内容。单个字符类中可以指定多个字符范围和明确字符,如下所示:
1 | multipleranges := [a-zA-Z=-] |
The above matches the characters in the range A to Z, a to z and the individual characters - and =.
上述内容匹配 A 到 Z、a 到 z 范围内的字符,以及单个字符 - 和 =。
Expressions can be made up of one or more expressions, such that one must be followed by the other. This is known as an implicit concatenation operator. For example, to satisfy the following rule, both A and B must be matched to satisfy the rule:
表达式可由一个或多个表达式构成,且这些表达式必须按顺序出现。这被称为隐式连接运算符。例如,要满足以下规则,必须同时匹配 A 和 B:
1 | symbol ::= A B |
Each expression must be matched once and only once, A followed by B. To support the description of repetition and optional match criteria, the postfix operators * and + are defined. * indicates that the preceding expression can be matched zero or more times. + indicates that the preceding expression must be matched one or more times. These appear in the following form:
每个表达式必须且只能被匹配一次,即 A 后接 B。为支持对重复匹配和可选匹配条件的描述,定义了后缀运算符 * 和 +。 表示其前面的表达式可被匹配零次或多次;+ 表示其前面的表达式必须被匹配一次或多次。这些运算符的形式如下:*
1 | zeroormore ::= expression* |
Parentheses are used to group expressions into a larger expression:
括号用于将多个表达式组合成一个更大的表达式:
1 | group ::= (A B) |
Like simpler expressions above, operators can be applied to groups, as well. To allow for alternates, we also define the infix operator |.
与上文所述的简单表达式类似,运算符也可应用于组合表达式。为支持选择匹配,我们还定义了中缀运算符 |。
1 | oneof ::= A | B |
The above indicates that the expression should match one of the expressions, A or B.
上述内容表明,该表达式应匹配其中一个表达式,即 A 或 B。
11.3.2 Precedence(优先级)
The operator precedence is in the following order:
运算符的优先级顺序如下:
- Terminals (literals and character classes)
- Grouping
() - Unary operators
+* - Concatenation
- Alternates
|
The precedence can be better described using grouping to show equivalents. Concatenation has higher precedence than alternates, such A B | C D is equivalent to (A B) | (C D). Unary operators have higher precedence than alternates and concatenation, such that A+ | B+ is equivalent to (A+) | (B+).
通过分组展示等价关系能更好地说明优先级规则。连接运算的优先级高于选择运算,例如 A B | C D 等价于 (A B) | (C D)。一元运算符的优先级高于选择运算和连接运算,因此 A+∣B+ 等价于 (A+) | (B+)。
11.3.3 Examples(示例)
The following combines the previous definitions to match a simple, relative path name, describing the individual components:
以下结合前面的定义来匹配一个简单的相对路径名,并对各个组成部分进行描述:
1 | path ::= component ("/" component)* |
The production “component” is one or more lowercase letters. A “path” is then at least one component, possibly followed by zero or more slash-component pairs. The above can be converted into the following regular expression:
“component”(组件)这一产生式由一个或多个小写字母构成。而 “path”(路径)则由至少一个组件组成,其后可能跟有零个或多个 “斜杠 - 组件” 对。上述内容可转换为如下正则表达式:
1 | [a-z]+(?:/[a-z]+)* |
OCI Image Implementations (OCI镜像实现)
Projects or Companies currently adopting the OCI Image Specification
目前采用 OCI 镜像规范的项目或企业
- projectatomic/skopeo
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) (announcement)
- Azure Container Registry (ACR)
- openSUSE/umoci
- cloudfoundry/grootfs (source)
- Mesos plans (design doc)
- Docker
- containerd/containerd
- Containers
- krustlet/oci-distribution
- box-builder/box
- coolljt0725/docker2oci
- regclient/regclient
- ORAS
11.4 Former Projects
OCI would like to recognize the following projects that are no longer actively maintained but have contributed to the adoption of OCI
OCI 希望对以下项目表示认可:这些项目虽已不再积极维护,但为 OCI 的推广应用做出了贡献。
- coreos/rkt - Project ended and archived on Feb 25, 2020
(to add your project please open a pull-request)